 |
|
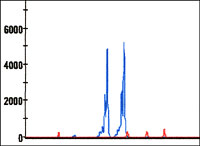
| Fragment analysis for the normal and premutation range in patients tested for Fragile X syndrome. The figure depicts results from a female with 19 and 29 CGG repeats in the 5’ UTR of the FMR1 gene. These repeat sizes are within the normal range. | |
Inherited Disorders
Cystic Fibrosis
The Stanford Molecular Pathology laboratory provides clinical diagnostic testing for CF. We currently offer carrier screening (basic and expanded), diagnostic testing, and molecular testing associated with CF newborn screening for the State of California. This testing includes a 40 mutation screening panel for all newborns in the State of California who have a high initial IRT enzyme test result. A subset of these, namely those for whom only one mutation was identified through panel testing, receive further screening by direct DNA sequencing.
Thalassemia
Hemoglobin disorders caused by an absence or reduction of one or more of the globin chains are called thalassemias. The hallmark of these autosomal recessive disorders is an imbalance of globin chain synthesis. For alpha thalassemia, we offer molecular genetic testing to evaluate the presence of the normal alpha 2 gene, identify the seven deletions most commonly encountered, and the alpha thalassemia mutation that results in Hemoglobin Constant Spring. In addition, comprehensive sequencing of the beta globin gene is offered.
Other Inherited Disorders
We also offer molecular genetic testing for achondroplasia and hypochondroplasia (skeletal disorders leading to short stature); craniosynostosis syndromes (associated with abnormal shape of the head); Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies; disorders associated with hearing loss (Connexin 26 and 30 related hearing loss and Pendred syndrome); disorders associated with intellectual disability (Fragile X and Prader-Willi syndromes); inherited diffuse gastric cancer; Huntington disease; biotinidase deficiency; hereditary hemochromatosis and additional other inherited conditions.

