Introduction :: SOLOMON ISLANDS
-
The UK established a protectorate over the Solomon Islands in the 1890s. Some of the bitterest fighting of World War II occurred on this archipelago. Self-government was achieved in 1976 and independence two years later. Ethnic violence, government malfeasance, endemic crime, and a narrow economic base have undermined stability and civil society. In June 2003, then Prime Minister Sir Allan KEMAKEZA sought the assistance of Australia in reestablishing law and order; the following month, an Australian-led multinational force arrived to restore peace and disarm ethnic militias. The Regional Assistance Mission to the Solomon Islands (RAMSI) has generally been effective in restoring law and order and rebuilding government institutions.
Geography :: SOLOMON ISLANDS
-
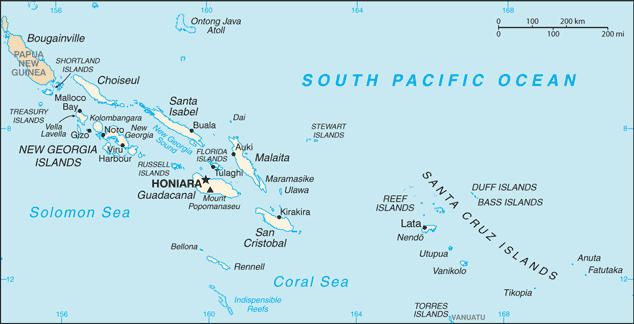
Oceania, group of islands in the South Pacific Ocean, east of Papua New Guinea
8 00 S, 159 00 E
Oceania
total: 28,896 sq km
land: 27,986 sq km
water: 910 sq km
country comparison to the world: 144
slightly smaller than Maryland
0 km
5,313 km
measured from claimed archipelagic baselines
territorial sea: 12 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm
tropical monsoon; few temperature and weather extremes
mostly rugged mountains with some low coral atolls
mean elevation: NA
elevation extremes: lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: Mount Popomanaseu 2,310 m
fish, forests, gold, bauxite, phosphates, lead, zinc, nickel
agricultural land: 3.9%
arable land 0.7%; permanent crops 2.9%; permanent pasture 0.3%
forest: 78.9%
other: 17.2% (2011 est.)
0 sq km NA (2012)
typhoons, but rarely destructive; geologically active region with frequent earthquakes, tremors, and volcanic activity; tsunamis
volcanism: Tinakula (elev. 851 m) has frequent eruption activity, while an eruption of Savo (elev. 485 m) could affect the capital Honiara on nearby Guadalcanal
deforestation; soil erosion; many of the surrounding coral reefs are dead or dying
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Environmental Modification, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Marine Life Conservation, Ozone Layer Protection, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
strategic location on sea routes between the South Pacific Ocean, the Solomon Sea, and the Coral Sea; on 2 April 2007 an undersea earthquake measuring 8.1 on the Richter scale occurred 345 km WNW of the capital Honiara; the resulting tsunami devastated coastal areas of Western and Choiseul provinces with dozens of deaths and thousands dislocated; the provincial capital of Gizo was especially hard hit
People and Society :: SOLOMON ISLANDS
-
635,027 (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
noun: Solomon Islander(s)
adjective: Solomon Islander
Melanesian 95.3%, Polynesian 3.1%, Micronesian 1.2%, other 0.3% (2009 est.)
Melanesian pidgin (in much of the country is lingua franca), English (official but spoken by only 1%-2% of the population), 120 indigenous languages
Protestant 73.4% (Church of Melanesia 31.9%, South Sea Evangelical 17.1%, Seventh Day Adventist 11.7%, United Church 10.1%, Christian Fellowship Church 2.5%), Roman Catholic 19.6%, other Christian 2.9%, other 4%, none 0.03%, unspecified 0.1% (2009 est.)
0-14 years: 35.13% (male 114,871/female 108,229)
15-24 years: 20.01% (male 65,349/female 61,702)
25-54 years: 36.12% (male 116,795/female 112,564)
55-64 years: 4.55% (male 14,565/female 14,302)
65 years and over: 4.2% (male 12,701/female 13,949) (2016 est.)
population pyramid:

Australia-Oceania
::SOLOMON ISLANDS

Population Pyramid
A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.
total dependency ratio: 75.1%
youth dependency ratio: 69.1%
elderly dependency ratio: 5.9%
potential support ratio: 16.8% (2015 est.)
total: 22.2 years
male: 22 years
female: 22.4 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 178
1.98% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
25.3 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
3.8 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 212
-1.7 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 156
urban population: 22.3% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 4.25% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
HONIARA (capital) 73,000 (2014)
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.04 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.92 male(s)/female
total population: 1.04 male(s)/female (2016 est.)
21.6
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2006/07 est.)
114 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
total: 15.2 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 17.3 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 12.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
total population: 75.3 years
male: 72.7 years
female: 78.1 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 108
3.22 children born/woman (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
34.6% (2006/07)
5.1% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 59
0.22 physicians/1,000 population (2009)
1.3 beds/1,000 population (2012)
improved:
urban: 93.2% of population
rural: 77.2% of population
total: 80.8% of population
unimproved:
urban: 6.8% of population
rural: 22.8% of population
total: 19.2% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 81.4% of population
rural: 15% of population
total: 29.8% of population
unimproved:
urban: 18.6% of population
rural: 85% of population
total: 70.2% of population (2015 est.)
NA
NA
NA
25% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 27
11.5% (2007)
country comparison to the world: 65
10% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 18
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 84.1%
male: 88.9%
female: 79.2% (2009 est.)
total: 9 years
male: 10 years
female: 9 years (2007)
Government :: SOLOMON ISLANDS
-
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: Solomon Islands
local long form: none
local short form: Solomon Islands
former: British Solomon Islands
etymology: Spanish explorer Alvaro de MENDANA named the isles in 1568 after the wealthy biblical King SOLOMON in the mistaken belief that the islands contained great riches
parliamentary democracy (National Parliament) under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm
name: Honiara
geographic coordinates: 9 26 S, 159 57 E
time difference: UTC+11 (16 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
9 provinces and 1 city*; Central, Choiseul, Guadalcanal, Honiara*, Isabel, Makira and Ulawa, Malaita, Rennell and Bellona, Temotu, Western
7 July 1978 (from the UK)
Independence Day, 7 July (1978)
adopted 31 May 1978, effective 7 July 1978; new constitution drafted in 2014 (2016)
mixed legal system of English common law and customary law
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; non-party state to the ICCt
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the Solomon Islands
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 7 years
21 years of age; universal
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General Frank KABUI (since 7 July 2009)
head of government: Prime Minister Manasseh SOGAVARE (since 9 December 2014)
cabinet: Cabinet appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister
elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch on the advice of the National Parliament for up to 5 years (eligible for a second term); following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually elected prime minister by the National Parliament; deputy prime minister appointed by the governor general on the advice of the prime minister from among members of the National Parliament
election results: Manasseh SOGAVARE (independent) elected prime minister; National Parliament vote - 31 to 19
description: unicameral National Parliament (50 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 4-year terms)
elections: last held on 19 November 2014 (next to be held in 2018)
election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - independents 32, DAP 7, UDP 5, PAP 3, KPSI 1, SIPFP 1, SIPRA 1
highest court(s): Court of Appeal (consists of the court president, and ex officio members to include the High Court chief justice and its puisne judges); High Court (consists of the chief justice and puisne judges as prescribed by the National Parliament)
judge selection and term of office: Court of Appeal and High Court president, chief justices, and puisne judges appointed by the governor-general upon recommendation of the Judicial and Legal Service Commission, chaired by the chief justice to include 5 members, mostly judicial officials and legal professionals; all judges appointed until retirement at age 60
subordinate courts: Magistrates' Courts; Customary Land Appeal Court; local courts
Democratic Alliance Party or DAP [Steve ABANA]
Kadere Party of Solomon Islands or KPSI [Alfred LEGUA]
People's Alliance Party or PAP [Nathaniel WAENA]
Solomon Islands People First Party or SIPFP [Jimmie RODGERS]
Solomon Islands Party for Rural Advancement or SIPRA [Manasseh MAELANGA]
United Democratic Party [Thomas Ko CHAN]
note: in general, Solomon Islands politics is characterized by fluid coalitions
Isatabu Freedom Movement or IFM
Malaita Eagle Force or MEF
note: these rival armed ethnic factions crippled the Solomon Islands in a wave of violence from 1999 to 2003
ACP, ADB, AOSIS, C, EITI (candidate country), ESCAP, FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IOC, ITU, MIGA, OPCW, PIF, Sparteca, SPC, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UPU, WFTU, WHO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Collin David BECK (since 31 March 2004)
chancery: 800 Second Avenue, Suite 400L, New York, NY 10017
telephone: [1] (212) 599-6192, 6193
FAX: [1] (212) 661-8925
the US does not have an embassy in the Solomon Islands; the US Ambassador to Papua New Guinea is accredited to the Solomon Islands
divided diagonally by a thin yellow stripe from the lower hoist-side corner; the upper triangle (hoist side) is blue with five white five-pointed stars arranged in an X pattern; the lower triangle is green; blue represents the ocean; green the land; and yellow sunshine; the five stars stand for the five main island groups of the Solomon Islands
national colors: blue, yellow, green, white
name: "God Save Our Solomon Islands"
lyrics/music: Panapasa BALEKANA and Matila BALEKANA/Panapasa BALEKANA
note: adopted 1978
Economy :: SOLOMON ISLANDS
-
The bulk of the population depends on agriculture, fishing, and forestry for at least part of its livelihood. Most manufactured goods and petroleum products must be imported. The islands are rich in undeveloped mineral resources such as lead, zinc, nickel, and gold. Prior to the arrival of The Regional Assistance Mission to the Solomon Islands (RAMSI), severe ethnic violence, the closure of key businesses, and an empty government treasury culminated in economic collapse. RAMSI's efforts to restore law and order and economic stability have led to modest growth as the economy rebuilds.
$1.198 billion (2016 est.)
$1.163 billion (2015 est.)
$1.127 billion (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 203
$1.218 billion (2015 est.)
3% (2016 est.)
3.3% (2015 est.)
2% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 95
$2,000 (2016 est.)
$2,000 (2015 est.)
$2,000 (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 205
18.7% of GDP (2016 est.)
17.1% of GDP (2015 est.)
14.9% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
agriculture: 52.8%
industry: 8%
services: 39.2% (2016 est.)
cocoa, coconuts, palm kernels, rice, fruit; cattle, pigs; fish; timber
fish (tuna), mining, timber
3.2% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 75
202,500 (2007 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
agriculture: 75%
industry: 5%
services: 20% (2000 est.)
NA%
NA%
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA%
revenues: $421.6 million
expenditures: $458.8 million (2016 est.)
34.6% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
-3.1% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 111
calendar year
2.4% (2016 est.) -0.6% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
10.1% (31 December 2016 est.)
10.48% (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 81
$445.1 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$405.7 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 169
$459.6 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$427.4 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 185
$98.3 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$84.69 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
-$54 million (2016 est.)
-$30 million (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
$419.9 million (2015 est.)
$419.9 million (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 176
timber, fish, copra, palm oil, cocoa
China 61.7%, India 5.9%, Italy 5.9% (2015)
$425.7 million (2015 est.)
$425.7 million (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
food, plant and equipment, manufactured goods, fuels, chemicals
Australia 24.7%, China 18.4%, Malaysia 6.3%, Singapore 5.8%, Fiji 4.7%, NZ 4.6%, Papua New Guinea 4.6% (2015)
$491.5 million (31 December 2013 est.)
$187.3 million (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 179
$545.6 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$522.1 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
$50.1 million (31 December 2016 est.)
$50.1 million (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 102
Solomon Islands dollars (SBD) per US dollar -
8.064 (2016 est.)
7.9147 (2015 est.)
7.9147 (2014 est.)
7.3754 (2013 est.)
7.36 (2012 est.)
Energy :: SOLOMON ISLANDS
-
85 million kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
79.05 million kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 201
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
37,000 kW (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199
100% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 190
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 205
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 136
0 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 202
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199
0 bbl (1 January 2016 es)
country comparison to the world: 207
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
1,600 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 198
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 209
1,554 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 195
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 206
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 199
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
0 cu m (1 January 2014 es)
country comparison to the world: 202
300,000 Mt (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
Communications :: SOLOMON ISLANDS
-
total subscriptions: 7,438
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 201
total: 425,000
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 68 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 174
domestic: mobile-cellular telephone density is about 65 per 100 persons
international: country code - 677; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Pacific Ocean) (2015)
Solomon Islands Broadcasting Corporation (SIBC) is the sole TV broadcaster with 1 station; multi-channel pay-TV is available; SIBC operates 2 national radio stations and 2 provincial stations; 2 local commercial radio stations; Radio Australia is availabl (2009)
.sb
total: 62,000
percent of population: 10% (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 187
Transportation :: SOLOMON ISLANDS
-
number of registered air carriers: 1
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 3
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 373,738
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 3,691,584 mt-km (2015)
H4 (2016)
36 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 109
total: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2013)
total: 35
1,524 to 2,437 m: 1
914 to 1,523 m: 10
under 914 m: 24 (2013)
3 (2013)
total: 1,390 km
paved: 34 km
unpaved: 1,356 km
note: includes 920 km of private plantation roads (2011)
country comparison to the world: 179
major seaport(s): Honiara, Malloco Bay, Viru Harbor, Tulaghi
Military and Security :: SOLOMON ISLANDS
-
no regular military forces; Royal Solomon Islands Police Force (2013)
Transnational Issues :: SOLOMON ISLANDS
-
since 2003, the Regional Assistance Mission to Solomon Islands, consisting of police, military, and civilian advisors drawn from 15 countries, has assisted in reestablishing and maintaining civil and political order while reinforcing regional stability and security
current situation: the Solomon Islands is a source and destination country for local adults and children and Southeast Asian men and women subjected to forced labor and forced prostitution; women from China, Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines are recruited for legitimate work and upon arrival are forced into prostitution; men from Indonesia and Malaysia recruited to work in the Solomon Islands’ mining and logging industries may be subjected to forced labor; local children are forced into prostitution near foreign logging camps, on fishing vessels, at hotels, and entertainment venues; some local children are also sold by their parents for marriage to foreign workers or put up for “informal adoption” to pay off debts and then find themselves forced into domestic servitude or forced prostitution
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – the Solomon Islands does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; in 2014, the Solomon Islands was granted a waiver from an otherwise required downgrade to Tier 3 because its government has a written plan that, if implemented, would constitute making significant efforts to bring itself into compliance with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; the government gazetted implementing regulations for the 2012 immigration act prohibiting transnational trafficking, but the penalties are not sufficiently stringent because they allow the option of paying a fine; a new draft law to address these weaknesses awaits parliamentary review; no new trafficking investigations were conducted, even after labor inspections at logging and fishing companies, no existing cases led to prosecutions or convictions, and no funding was allocated for national anti-trafficking efforts; authorities did not identify or protect any victims and lack any procedures or shelters to do so; civil society and religious organizations provide most of the limited services available; a lack of understanding of the crime of trafficking remains a serious challenge (2015)