Introduction :: NEW ZEALAND
-
The Polynesian Maori reached New Zealand in about A.D. 800. In 1840, their chieftains entered into a compact with Britain, the Treaty of Waitangi, in which they ceded sovereignty to Queen Victoria while retaining territorial rights. That same year, the British began the first organized colonial settlement. A series of land wars between 1843 and 1872 ended with the defeat of the native peoples. The British colony of New Zealand became an independent dominion in 1907 and supported the UK militarily in both world wars. New Zealand's full participation in a number of defense alliances lapsed by the 1980s. In recent years, the government has sought to address longstanding Maori grievances. New Zealand assumed a nonpermanent seat on the UN Security Council for the 2015-16 term.
Geography :: NEW ZEALAND
-
Oceania, islands in the South Pacific Ocean, southeast of Australia
41 00 S, 174 00 E
Oceania
total: 268,838 sq km
land: 264,537 sq km
water: 4,301 sq km
note: includes Antipodes Islands, Auckland Islands, Bounty Islands, Campbell Island, Chatham Islands, and Kermadec Islands
country comparison to the world: 76
almost twice the size of North Carolina; about the size of Colorado
Area comparison map:

Australia-Oceania
::NEW ZEALAND

Area Comparison
almost twice the size of North Carolina; about the size of Colorado
0 km
15,134 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
continental shelf: 200 nm or to the edge of the continental margin
temperate with sharp regional contrasts
predominately mountainous with large coastal plains
mean elevation: 388 m
elevation extremes: lowest point: Pacific Ocean 0 m
highest point: Aoraki-Mount Cook 3,754 m
natural gas, iron ore, sand, coal, timber, hydropower, gold, limestone
agricultural land: 43.2%
arable land 1.8%; permanent crops 0.3%; permanent pasture 41.1%
forest: 31.4%
other: 25.4% (2011 est.)
7,210 sq km (2012)
earthquakes are common, though usually not severe; volcanic activity
volcanism: significant volcanism on North Island; Ruapehu (elev. 2,797 m), which last erupted in 2007, has a history of large eruptions in the past century; Taranaki has the potential to produce dangerous avalanches and lahars; other historically active volcanoes include Okataina, Raoul Island, Tongariro, and White Island
deforestation; soil erosion; native flora and fauna hard-hit by invasive species
party to: Antarctic-Environmental Protocol, Antarctic-Marine Living Resources, Antarctic Treaty, Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Marine Dumping, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands, Whaling
signed, but not ratified: Antarctic Seals, Marine Life Conservation
almost 90% of the population lives in cities; Wellington is the southernmost national capital in the world
People and Society :: NEW ZEALAND
-
4,474,549 (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 126
noun: New Zealander(s)
adjective: New Zealand
European 71.2%, Maori 14.1%, Asian 11.3%, Pacific peoples 7.6%, Middle Eastern, Latin American, African 1.1%, other 1.6%, not stated or unidentified 5.4%
note: based on the 2013 census of the usually resident population; percentages add up to more than 100% because respondents were able to identify more than one ethnic group (2013 est.)
English (de facto official) 89.8%, Maori (de jure official) 3.5%, Samoan 2%, Hindi 1.6%, French 1.2%, Northern Chinese 1.2%, Yue 1%, other or not stated 20.5%, New Zealand Sign Language (de jure official)
note: shares sum to 120.8% due to multiple responses on census (2013 est.)
Christian 44.3% (Catholic 11.6%, Anglican 10.8%, Presbyterian and Congregational 7.8%, Methodist, 2.4%, Pentecostal 1.8%, other 9.9%), Hindu 2.1%, Buddhist 1.4%, Maori Christian 1.3%, Islam 1.1%, other religion 1.4% (includes Judaism, Spiritualism and New Age religions, Baha'i, Asian religions other than Buddhism), no religion 38.5%, not stated or unidentified 8.2%, objected to answering 4.1%
note: based on the 2013 census of the usually resident population; percentages add up to more than 100% because people were able to identify more than one religion (2013 est.)
0-14 years: 19.76% (male 452,810/female 431,198)
15-24 years: 13.56% (male 312,032/female 294,662)
25-54 years: 40.05% (male 897,549/female 894,394)
55-64 years: 11.7% (male 255,381/female 268,012)
65 years and over: 14.94% (male 308,949/female 359,562) (2016 est.)
population pyramid:

Australia-Oceania
::NEW ZEALAND

Population Pyramid
A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.
total dependency ratio: 54%
youth dependency ratio: 31.1%
elderly dependency ratio: 22.9%
potential support ratio: 4.4% (2015 est.)
total: 37.8 years
male: 36.9 years
female: 38.7 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
0.8% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 137
13.3 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
7.4 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
2.2 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
urban population: 86.3% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 1.05% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
Auckland 1.344 million; WELLINGTON (capital) 383,000 (2015)
at birth: 1.05 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.05 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1.06 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/female
total population: 0.99 male(s)/female (2016 est.)
27.8
note: median age at first birth (2009 est.)
11 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 144
total: 4.5 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 5 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 3.9 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
total population: 81.2 years
male: 79.1 years
female: 83.3 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 28
2.03 children born/woman (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
11% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 20
2.74 physicians/1,000 population (2010)
2.3 beds/1,000 population (2011)
improved:
urban: 100% of population
rural: 100% of population
total: 100% of population
unimproved:
urban: 0% of population
rural: 0% of population
total: 0% of population (2015 est.)
NA
NA
NA
30.6% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 34
6.3% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 16
total: 19 years
male: 18 years
female: 20 years (2014)
total: 15%
male: 14.3%
female: 15.8% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 64
Government :: NEW ZEALAND
-
conventional long form: none
conventional short form: New Zealand
abbreviation: NZ
etymology: Dutch explorer Abel TASMAN was the first European to reach New Zealand in 1642; he named it Staten Landt, but Dutch cartographers renamed it Nova Zeelandia in 1645 after the Dutch province of Zeeland; British explorer Captain James COOK subsequently anglicized the name to New Zealand when he mapped the islands in 1769
parliamentary democracy (New Zealand Parliament) under a constitutional monarchy; a Commonwealth realm
name: Wellington
geographic coordinates: 41 18 S, 174 47 E
time difference: UTC+12 (17 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
daylight saving time: +1hr, begins last Sunday in September; ends first Sunday in April
note: New Zealand has two time zones - New Zealand standard time (12 hours in advance of UTC), and Chatham Islands time (45 minutes in advance of New Zealand standard time)
16 regions and 1 territory*; Auckland, Bay of Plenty, Canterbury, Chatham Islands*, Gisborne, Hawke's Bay, Manawatu-Wanganui, Marlborough, Nelson, Northland, Otago, Southland, Taranaki, Tasman, Waikato, Wellington, West Coast
Cook Islands, Niue, Tokelau
26 September 1907 (from the UK)
Waitangi Day (Treaty of Waitangi established British sovereignty over New Zealand), 6 February (1840); ANZAC Day (commemorated as the anniversary of the landing of troops of the Australian and New Zealand Army Corps during World War I at Gallipoli, Turkey), 25 April (1915)
Constitution Act 1986 (the principal formal charter) adopted and effective 1 January 1987; amended 1999, 2005, 2014 (2016)
common law system, based on English model, with special legislation and land courts for the Maori
accepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of New Zealand
dual citizenship recognized: yes
residency requirement for naturalization: 3 years
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: Queen ELIZABETH II (since 6 February 1952); represented by Governor General Dame Patricia Lee REDDY (since 28 September 2016)
head of government: Prime Minister Simon William "Bill" ENGLISH (since 12 December 2016); December 2016; Deputy Prime Minister Paula BENNETT (since 12 December 2016); note - Prime Minister John KEY (since 19 November 2008) resigned effective 12 December 2016
cabinet: Executive Council appointed by the governor general on the recommendation of the prime minister
elections/appointments: the monarchy is hereditary; governor general appointed by the monarch; following legislative elections, the leader of the majority party or majority coalition usually appointed prime minister by the governor general; deputy prime minister appointed by the governor general
description: unicameral House of Representatives - commonly called Parliament (usually 120 seats; 70 members directly elected in single-seat constituencies, including 7 Maori constituencies, by simple majority vote and 50 directly elected by proportional representation vote; members serve 3-year terms)
elections: last held on 20 September 2014 (next to be held by September 2017)
election results: percent of vote by party - National Party 47%, Labor Party 25.1%, Green Party 10.7%, NZ First 8.7%, Maori 1.3%, ACT Party .7%, United Future .2%, other 6.3%; seats by party - National Party 60, Labor Party 32, Green Party 14, NZ First 11, Maori 2, ACT Party 1, United Future 1
highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of 5 justices including the chief justice); note - the Supreme Court in 2004 replaced the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council in London as the final appeals court
judge selection and term of office: justices appointed by the governor-general on the recommendation of the attorney-general; justices appointed for life
subordinate courts: Court of Appeal; High Court; tribunals and authorities; district courts; specialized courts for issues related to employment, environment, Maori lands, and military
ACT New Zealand [Rodney HIDE]
Green Party [Russel NORMAN and Metiria TUREI]
Jim Anderton's Progressive Party [James (Jim) ANDERTON]
Mana Party [Hone HARAWIRA]
Maori Party [Tariana TURIA and Dr. Pita SHARPLES]
New Zealand First Party or NZ First [Winston PETERS]
New Zealand Labor Party [Phil GOFF]
New Zealand National Party [John KEY]
United Future New Zealand [Peter DUNNE]
Women's Electoral Lobby or WEL
other: apartheid groups; civil rights groups; farmers groups; Maori; nuclear weapons groups; women's rights groups
ADB, ANZUS (US suspended security obligations to NZ on 11 August 1986), APEC, ARF, ASEAN (dialogue partner), Australia Group, BIS, C, CD, CP, EAS, EBRD, FAO, FATF, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IEA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, IHO, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NSG, OECD, OPCW, Pacific Alliance (observer), Paris Club (associate), PCA, PIF, SICA (observer), Sparteca, SPC, UN, UN Security Council (temporary), UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNMISS, UNTSO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Timothy John GROSER (since 28 January 2016)
chancery: 37 Observatory Circle NW, Washington, DC 20008
telephone: [1] (202) 328-4800
FAX: [1] (202) 667-5227[1] (202) 667-5227
consulate(s) general: Honolulu (HI), Los Angeles, New York
chief of mission: Ambassador Mark GILBERT (since 9 February 2015) note - also accredited to Samoa
embassy: 29 Fitzherbert Terrace, Thorndon, Wellington
mailing address: P. O. Box 1190, Wellington; PSC 467, Box 1, APO AP 96531-1034
telephone: [64] (4) 462-6000
FAX: [64] (4) 499-0490
consulate(s) general: Auckland
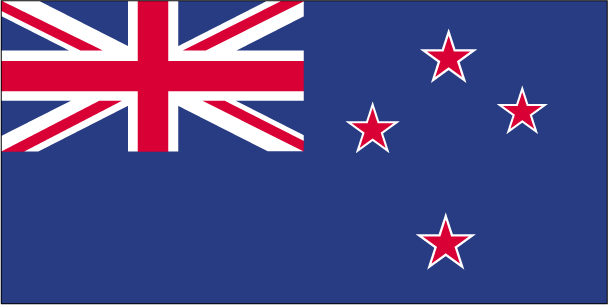
blue with the flag of the UK in the upper hoist-side quadrant with four red five-pointed stars edged in white centered in the outer half of the flag; the stars represent the Southern Cross constellation
Southern Cross constellation (four, five-pointed stars), kiwi (bird), silver fern; national colors: black, white, red (ochre)
name: "God Defend New Zealand"
lyrics/music: Thomas BRACKEN [English], Thomas Henry SMITH [Maori]/John Joseph WOODS
note: adopted 1940 as national song, adopted 1977 as co-national anthem; New Zealand has two national anthems with equal status; as a commonwealth realm, in addition to "God Defend New Zealand," "God Save the Queen" serves as a national anthem (see United Kingdom); "God Save the Queen" normally played only when a member of the royal family or the governor-general is present; in all other cases, "God Defend New Zealand" is played
Economy :: NEW ZEALAND
-
Over the past 30 years, the government has transformed New Zealand from an agrarian economy, dependent on concessionary British market access, to a more industrialized, free market economy that can compete globally. This dynamic growth has boosted real incomes - but left behind some at the bottom of the ladder - and broadened and deepened the technological capabilities of the industrial sector.
Per capita income rose for ten consecutive years until 2007 in purchasing power parity terms, but fell in 2008-09. Debt-driven consumer spending drove robust growth in the first half of the decade, fueling a large balance of payments deficit that posed a challenge for policymakers. Inflationary pressures caused the central bank to raise its key rate steadily from January 2004 until it was among the highest in the OECD in 2007-08. The higher rate attracted international capital inflows, which strengthened the currency and housing market while aggravating the current account deficit.
The economy fell into recession before the start of the global financial crisis and contracted for five consecutive quarters in 2008-09. In line with global peers, the central bank cut interest rates aggressively and the government developed fiscal stimulus measures. The economy pulled out of recession in 2009, and achieved 2%-3% growth from 2011 to 2015. Nevertheless, key trade sectors remain vulnerable to weak external demand and lower commodity prices. In the aftermath of the 2010 Canterbury earthquakes, the government has continued programs to expand export markets, develop capital markets, invest in innovation, raise productivity growth, and develop infrastructure, while easing its fiscal austerity.
$174.8 billion (2016 est.)
$170.1 billion (2015 est.)
$165.2 billion (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 68
$179.4 billion (2015 est.)
2.8% (2016 est.)
3% (2015 est.)
3% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 103
$37,100 (2016 est.)
$36,600 (2015 est.)
$36,300 (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 50
20.3% of GDP (2016 est.)
19.8% of GDP (2015 est.)
19.4% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 82
household consumption: 57.4%
government consumption: 18.5%
investment in fixed capital: 23.5%
investment in inventories: 0.3%
exports of goods and services: 26.7%
imports of goods and services: -26.4% (2016 est.)
agriculture: 4.2%
industry: 26.5%
services: 69.2% (2016 est.)
dairy products, sheep, beef, poultry, fruit, vegetables, wine, seafood, wheat and barley
agriculture, forestry, fishing, logs and wood articles, manufacturing, mining, construction, financial services, real estate services, tourism
2.6% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 90
2.562 million (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 114
agriculture: 7%
industry: 19%
services: 74% (2006 est.)
5.1% (2016 est.)
5.4% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 55
NA%
lowest 10%: NA%
highest 10%: NA%
36.2 (1997)
country comparison to the world: 85
revenues: $67.61 billion
expenditures: $67.01 billion (2016 est.)
37.7% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
0.3% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 26
34% of GDP (2016 est.)
35% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 133
1 April - 31 March
note: this is the fiscal year for tax purposes
0.6% (2016 est.)
0.3% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
2.5% (31 December 2009)
5% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 107
5% (31 December 2016 est.)
5.76% (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 143
$34.99 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$31.58 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
$115 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$102.8 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 54
$373.8 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$342.4 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 31
$74.35 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$74.42 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
$65.96 billion (31 December 2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 45
-$5.385 billion (2016 est.)
-$5.594 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171
$31.96 billion (2016 est.)
$34.41 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
dairy products, meat and edible offal, logs and wood articles, fruit, crude oil, wine
China 17.5%, Australia 16.9%, US 11.8%, Japan 6% (2015)
$34.83 billion (2016 est.)
$35.8 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 59
petroleum and products, mechanical machinery, vehicles and parts, electrical machinery, textiles
China 19.4%, Australia 11.8%, US 11.7%, Japan 6.6%, Germany 4.7%, Thailand 4.2% (2015)
$18.55 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$14.7 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
$81.39 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$83.4 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
$71.19 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$74.17 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 53
$59.08 billion (31 December 2009)
country comparison to the world: 41
New Zealand dollars (NZD) per US dollar -
1.441 (2016 est.)
1.4279 (2015 est.)
1.4279 (2014 est.)
1.2039 (2013 est.)
1.23 (2012 est.)
Energy :: NEW ZEALAND
-
43 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 58
40 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 56
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
0 kWh (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 149
9.7 million kW (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
29% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 88
55.2% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 43
15.8% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 18
41,280 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 61
34,090 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 47
104,700 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
67.2 million bbl (1 January 2016 es)
country comparison to the world: 78
119,300 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 67
160,700 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 63
5,345 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
46,360 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 84
5.241 billion cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
5.387 billion cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 57
0 cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 109
0 cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 196
36.9 billion cu m (1 January 2016 es)
country comparison to the world: 66
37 million Mt (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 72
Communications :: NEW ZEALAND
-
total subscriptions: 1.85 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 42 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 62
total: 5.6 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 126 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 116
general assessment: excellent domestic and international systems
domestic: combined fixed-line and mobile-cellular telephone subscribership exceeds 160 per 100 persons
international: country code - 64; the Southern Cross submarine cable system provides links to Australia, Fiji, and the US; satellite earth stations - 8 (1 Inmarsat - Pacific Ocean, 7 other) (2015)
state-owned Television New Zealand operates multiple TV networks and state-owned Radio New Zealand operates 3 radio networks and an external shortwave radio service to the South Pacific region; a small number of national commercial TV and radio stations a (2008)
.nz
total: 3.916 million
percent of population: 88.2% (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 77
Transportation :: NEW ZEALAND
-
number of registered air carriers: 6
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 123
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 15,304,409
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 999,384,961 mt-km (2015)
ZK (2016)
123 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 48
total: 39
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 12
914 to 1,523 m: 23
under 914 m: 1 (2013)
total: 84
1,524 to 2,437 m: 3
914 to 1,523 m: 33
under 914 m: 48 (2013)
condensate 331 km; gas 1,936 km; liquid petroleum gas 172 km; oil 288 km; refined products 198 km (2013)
total: 4,128 km
narrow gauge: 4,128 km 1.067-m gauge (503 km electrified) (2014)
country comparison to the world: 42
total: 94,902 km
paved: 62,759 km (includes 199 km of expressways)
unpaved: 32,143 km (2012)
country comparison to the world: 52
total: 15
by type: bulk carrier 3, cargo 3, chemical tanker 1, container 1, passenger/cargo 5, petroleum tanker 2
foreign-owned: 7 (Germany 2, Hong Kong 1, South Africa 1, Switzerland 2, UK 1)
registered in other countries: 5 (Antigua and Barbuda 2, Cook Islands 2, Samoa 1) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 101
major seaport(s): Auckland, Lyttelton, Manukau Harbor, Marsden Point, Tauranga, Wellington
Military and Security :: NEW ZEALAND
-
New Zealand Defense Force (NZDF): New Zealand Army, Royal New Zealand Navy, Royal New Zealand Air Force (Te Hokowhitu o Kahurangi, RNZAF) (2013)
17 years of age for voluntary military service; soldiers cannot be deployed until the age of 18; no conscription; 3 years of secondary education required; must be a citizen of NZ, the UK, Australia, Canada, or the US, and resident of NZ for the previous 5 years (2013)
1.13% of GDP (2012)
1.12% of GDP (2011)
1.13% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 87
Transnational Issues :: NEW ZEALAND
-
asserts a territorial claim in Antarctica (Ross Dependency)
significant consumer of amphetamines