Azad Kashmir
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
| Azad Jammu and Kashmir (AJK) آزاد جموں و کشمیر |
|
 |
 |
| Country |
|
| Capital Coordinates |
Muzaffarabad 34°13′N 73°17′E / 34.22°N 73.28°E |
| Largest city | Mirpur |
| Population (2008) • Density |
4,567,982 (estimate) • 306/km² |
| Area |
13,297 km² |
| Time zone | PST (UTC+5) |
| Main language(s) | Urdu (official) Pahari Mirpuri Gojri Hindko Punjabi Pashto |
| Status | self-governing state under Pakistani control [1] |
| Districts | 8 |
| Towns | 19 |
| Union councils | 182 |
| Established | 1948 |
| Governor/Commissioner | President Raja Zulqarnain Khan |
| Chief Minister | Prime Minister Raja Farooq Haider Khan |
| Legislature (seats) | Legislative Assembly (49) |
| Website | Government of Azad Kashmir |
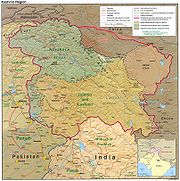
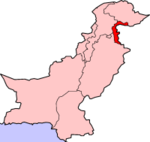
Azad Jammu and Kashmir (Urdu: آزاد جموں و کشمیر; AJK) or Azad Kashmir for short (literally, "Free Kashmir"), is the southernmost political entity within the Pakistani-controlled part of the former princely state of Jammu and Kashmir. It borders the present-day Indian-administered state of Jammu and Kashmir to the east (separated from it by the Line of Control), the North-West Frontier Province of Pakistan to the west, the Federally Administered Northern Areas (FANA) to the north, and the Punjab Province of Pakistan to the south. With its capital at Muzaffarabad, Azad Kashmir covers an area of 13,297 square kilometres (5,134 sq mi) and has an estimated population of about four million.
Azad Kashmir's financial matters, i.e., budget and tax affairs, are dealt with by the Azad Jammu and Kashmir Council, rather than by Pakistan's Central Board of Revenue. The Azad Jammu and Kashmir Council is a supreme body consisting of 11 members, six from the government of Azad Jammu and Kashmir and five from the government of Pakistan. Its chairman/chief executive is the president of Pakistan. Other members of the council are the president and the prime minister of Azad Kashmir and a few other AJK ministers.[2][3]
Contents |
History
After the Partition of India in 1947, the princely states were given the option of joining either India or Pakistan. However, Hari Singh, the maharaja of Jammu and Kashmir, wanted Jammu and Kashmir to remain independent. In order to buy some time, he signed a stand-still agreement, which sidestepped the agreement that each princely state would join either India or Pakistan.[4] The raiders from North-West Frontier Province and the Tribal Areas feared that Hari Singh might join Indian Union. In October 1947, supported by the Pakistani Army, they attacked Kashmir and tried to take over control of Kashmir. Initially Hari Singh tried to resist their progress but failed. Hari Singh then requested Indian Union to help. India responded that it could not help unless Kashmir joined India. So on 26 October 1947, Kashmir accession papers were signed and Indian troops were airlifted to Srinagar. Fighting ensued between the Indian Army and Pakistani Army, with control stabilizing more or less around what is now the "Line of Control".[5]
Later, India approached the United Nations to solve the dispute and resolutions were passed to hold a plebiscite with regard to Kashmir's future. However, this plebiscite has not been held on either side, since the legal requirement for the holding of a plebiscite was the withdrawal of the Indian and Pakistani armies from the parts of Kashmir that were under their respective control—a withdrawal that never did take place.[6] In 1949, a cease-fire line separating the Indian- and Pakistani-controlled parts of Kashmir was formally put into effect.
Following the 1949 cease-fire agreement, the government of Pakistan divided the northern and western parts of Kashmir which it held into the following two separately-controlled political entities:
- Azad Jammu and Kashmir (AJK) - the narrow southern part, 250 miles (400 km) long, with a width varying from 10 to 40 miles (16 to 64 km).
- Gilgit-Baltistan formerly called Federally Administered Northern Areas (FANA) - is the much larger area to the north of AJK, 72,496 square kilometres (27,991 sq mi); it was directly administered by Pakistan as a de facto dependent territory, i.e., a non-self-governing territory. However it was officially granted full autonomy on August 29, 2009.[7]
An area of Kashmir that was once under Pakistani control is the Shaksgam tract—a small region along the northeastern border of the Northern Areas that was provisionally ceded by Pakistan to the People's Republic of China in 1963 and which now forms part of China's Uygur Autonomous Region of Xinjiang.
In 1972, the then-current border between Pakistani and Indian, which held areas of Kashmir, was designated as the "Line of Control". The Line of Control has remained unchanged[8] since the 1972 Simla Agreement, which bound the two countries "to settle their differences by peaceful means through bilateral negotiations." Some political experts claim that, in view of that pact, the only solution to the issue is mutual negotiation between the two countries without involving a third party, such as the United Nations.
A devastating earthquake hit Azad Kashmir called the Kashmir earthquake in 2005.
Government
Azad Jammu and Kashmir (AJK) is a self-governing state under Pakistani control but is not constitutionally part of Pakistan.[9][10] It has its own elected president, prime minister, legislature, high court, and official flag. The government of Pakistan has not yet allowed the state to issue its own postage stamps, however, and Pakistani stamps are used in the state instead. The state is administratively divided into two divisions which, in turn, are divided into eight districts.
| Division | District | Area (km²) | Population (1998) | Headquarters |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mirpur | Bhimber | 1,516 | 301,633 | Bhimber |
| Kotli | 1,862 | 563,094 | Kotli | |
| Mirpur | 1,010 | 333,482 | Mirpur | |
| Muzaffarabad | Muzaffarabad [11] | 2,496 | 638,973 | Muzaffarabad |
| Neelum[12] | 3,621 | 106,778 | Athmuqam | |
| Poonch | Poonch | 855 | 411,035 | Rawalakot [13] |
| Bagh | 1,368 | 393,415 | Bagh | |
| Sudhnati | 569 | 334,091 | Pallandari | |
| AJK total | 8 districts | 13,297 | 2,972,501 | Muzaffarabad |
A 2008 report by the United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees determined that Pakistan-administered Kashmir was 'not free'.[14]
There are roughly 1.5 million refugees from Indian Administered Kashmir in Azad Kashmir and Pakistan.
Ethnic groups
Azad Kashmir is predominantly Muslim. The majority of the population is culturally, linguistically, and ethnically related to the people of northern Punjab. The article Ethnic groups of Azad Kashmir gives a breakdown of all the major tribes in the state. The vast majority of the people who live in Azad Kashmir, despite that region being referred to as part of Kashmir, do not speak Kashmiri or any of its dialects.
Languages
Urdu is the official language of Azad Kashmir but is spoken by only a minority of people.[citation needed] The dominant language spoken in the state is Pahari, which is very similar to Pothwari and Hindko.[citation needed]
Economy and Resources
| This section requires expansion. |
In the 1950's economic development began [15]then later in the 1960's with the contruction of the Mangla Damthe Azad Jammu and Kashmir Government get royalties from the Pakistani government for electricity it provides to the nation from Mangla Dam in Mirpur in Kashmir.
Agriculture is a part of Azad Kashmir's economy; low-lying areas that have high populations grow crops like barley, millet, corn (maize), and wheat, and also raise cattle. In the more elevated areas that are less populated and are spread out, foresty, corn and livestock are the source of living.
Thier are some mineral and marble resources in Azad Kashmir close to Mirpur and Muzaffarabad; there are also some graphite deposits at Mohriwali. There are some reservoirs of low-grade coal, chalk, bauxite, and zircon. Local household industries produce carved wooden objects, textiles, and dhurrie carpets.[16] There is also an art and craft industry that produces such cultural goods as: namdas, shawls, pashmina, pherans, papier mache, basketry copper, rugs, wood carving, silk and woolen clothing, patto, carpet, namda gubba and silverware. Agricultural goods produced in the region include: mushrooms, honey, walnuts, apples, cherries, medicinal herbs and plants, resin, deodar, kail, chir, fir, maple and ash timber.[17][18][19]
In addition to agriculture, textiles, arts and crafts, remittances have played a major role in the economy of Azad Kashmir. One analyst estimated that the figure for Azad Kashmir was 25.1% in 2001; for household annual income, those people living in higher areas are more dependent on remittance than lower areas.[20]
In the latter part of 2006, billions of dollars for development were mooted by international aid agencies for the reconstruction and rehabilitation of earthquake-hit zones in Azad Kashmir, though much of that amount was subsequently lost in bureaucratic channels, leading to delay in help reaching the most needy, and hundreds of people continued to live in tents long after the earthquake.[21] A land-use plan for the city of Muzaffarabad was prepared by the Japan International Cooperation Agency.
Education
The literacy rate in Azad Kashmir was 62% in 2004, higher than in any other region in Pakistan.[22] However, only 2.2% were graduates, compared to the average of 2.9% for the whole of Pakistan.[23]
Gallery
|
|
This section looks like an image gallery. Wikipedia policy discourages galleries of random images of the article subject; please edit or remove the section accordingly, moving freely licensed images to Wikimedia Commons if not already hosted there. (January 2009) |
State symbols
|
Black-necked crane, the state bird |
Kashmir stag, the state animal |
Almond tree, the state tree |
Rhododendron, the state flower |
|
Polo, the state sport |
Notable Kashmiris
- Mian Muhammad Bakhsh, Sufi saint
- Sardar Sikandar Hayat Khan, former prime minister and president of Azad Kashmir
- Raja Habib ur Rahman Khan, freedom fighter in the Indian National Army from Azad Kashmir; conquered Bhimber in the Indo-Pakistani War of 1947; Pakistan Secretary of Defense; member of Azad Kashmir Council
- Mohammad Sharif Chattar, botanist, author, poet
- Baba Shadi Shaheed, Sufi saint
- Barrister Sultan Mahmood, former prime minister of Azad Kashmir
- Lord Nazir Ahmed, member of the UK House of Lords
- Karam Hussain, mayor of Kirklees, UK
- Ghulam Ahmad, author, educator, and philanthropist
- Khawaja Zafar Iqbal, journalist
- Ali Adnan Ibrahim, scholar and lawyer
- Saira Khan, BBC presenter
- Khalid Mahmood, member of the UK parliament
- Sheikh Younas Azam, Kashmiri journalist (deceased)
- Tassadaq Hussain Khan, former army chief
- Baba-e-Poonch Khansahib Col Khan Muhammad Khan, member of Legislative Assembly for Tehsil Bagh and Sudhonoti, 1934 - 1946
- Sardar Fateh Muhammad Khan Karelvi, Muslim MLA during Dogra rule
- Aziz Khan, former chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff Committee of Pakistan
- Sardar Muhammad Anwar Khan, vice-chief of the General Staff
- General Raja Sakhi Daler Khan
- Tahir Abbas, sociologist at the University of Birmingham
See also
References
- ^ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/46696/Azad-Kashmir#
- ^ http://www.ajk.gov.pk/site/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=2257&Itemid=144
- ^ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/46696/Azad-Kashmir#.
- ^ http://www.indiatogether.org/peace/kashmir/intro.htm
- ^ South Asian Journal
- ^ UNCIP Resolution of August 13, 1948 (S/1100) - Embassy of India, Washington, DC
- ^ http://www.daily.pk/pakistan-grants-full-autonomy-to-northern-areas-9753/
- ^ UNMOGIP: United Nations Military Observer Group in India and Pakistan
- ^ http://www.ajk.gov.pk/site/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=2257&Itemid=144
- ^ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/46696/Azad-Kashmir#.
- ^ http://www.eurojournals.com/ejsr%2017%203.pdf#page=89
- ^ Official website, Government of Azad Kashmir. ""Facts and Figures"". http://www.ajk.gov.pk/site/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=2256&Itemid=144. Retrieved 2006-04-19. - Neelum is a recently created district and no figures are available as yet.
- ^ http://www.eurojournals.com/ejsr%2017%203.pdf#page=89
- ^ Freedom in the World 2008 - Kashmir (Pakistan), United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees, 2008-07-02
- ^ [1]
- ^ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/46696/Azad-Kashmir#
- ^ http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/46696/Azad-Kashmir#
- ^ http://www.ajk.gov.pk/site/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=2254&Itemid=144
- ^ http://www.ajk.gov.pk/tourism/administrative.html
- ^ http://www.sdpi.org/whats_new/recent_publications/BGPaper_Remittances_Pakistan.pdf
- ^ Rs1.25 trillion to be spent in Azad Kashmir: Reconstruction in quake-hit zone - Dawn Pakistan
- ^ Literacy Rate in Azad Kashmir nearly 62 pc
- ^ http://www.dailytimes.com.pk/default.asp?page=story_17-4-2005_pg7_37 - 7th Paragraph.
External links
Find more about Azad Kashmir on Wikipedia's sister projects:
- Government of Azad Jammu and Kashmir
- Azad Jammu and Kashmir travel guide from Wikitravel
- "Azad Kashmir" article at Encyclopædia Britannica
- Eurojournals page about dwellings in Azad Kashmir
- Azad Jammu and Kashmir Council website
- Azad Jammu Kashmir Tourism site
- Lonely Planet tourist guide to Azad Kashmir with brief facts
- Another Lonely Planet tourist guide to Azad Kashmir with brief facts
- World atlas page about Azad Kashmir status
- About Azad Kashmir
- An academic introduction to Azad Kashmir
- Overview of hydropower potential in Azad Jammu & Kashmir
- Paper examining the integration of disaster relief efforts during the 2005 Kashmir earthquake relief effort
- Azad Jammu & Kashmir Community Development Program
- Maps of Azad Jammu and Kashmir
- Crafts of Kashmir
- Prime Minister of Azad Jammu and Kashmir site
- Planning and Development Department of Azad Jammu and Kashmir
|
|||||||||||
|
||||||||||