


Africa :: GHANA
Introduction :: GHANA
-
Formed from the merger of the British colony of the Gold Coast and the Togoland trust territory, Ghana in 1957 became the first sub-Saharan country in colonial Africa to gain its independence. Ghana endured a long series of coups before Lt. Jerry RAWLINGS took power in 1981 and banned political parties. After approving a new constitution and restoring multiparty politics in 1992, RAWLINGS won presidential elections in 1992 and 1996 but was constitutionally prevented from running for a third term in 2000. John KUFUOR succeeded him and was reelected in 2004. John Atta MILLS won the 2008 presidential election and took over as head of state, but he died in July 2012 and was constitutionally succeeded by his vice president, John Dramani MAHAMA, who subsequently won the December 2012 presidential election.
Geography :: GHANA
-
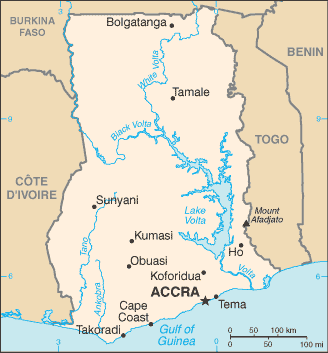
Western Africa, bordering the Gulf of Guinea, between Cote d'Ivoire and Togo8 00 N, 2 00 WAfricatotal: 238,533 sq kmland: 227,533 sq kmwater: 11,000 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 82slightly smaller than Oregontotal: 2,420 kmborder countries (3): Burkina Faso 602 km, Cote d'Ivoire 720 km, Togo 1,098 km539 kmterritorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive economic zone: 200 nmcontinental shelf: 200 nmtropical; warm and comparatively dry along southeast coast; hot and humid in southwest; hot and dry in northmostly low plains with dissected plateau in south-central areamean elevation: 190 melevation extremes: lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 mhighest point: Mount Afadjato 885 mgold, timber, industrial diamonds, bauxite, manganese, fish, rubber, hydropower, petroleum, silver, salt, limestoneagricultural land: 69.1%arable land 20.7%; permanent crops 11.9%; permanent pasture 36.5%forest: 21.2%other: 9.7% (2011 est.)340 sq km (2012)dry, dusty, northeastern harmattan winds from January to March; droughtsrecurrent drought in north severely affects agricultural activities; deforestation; overgrazing; soil erosion; poaching and habitat destruction threatens wildlife populations; water pollution; inadequate supplies of potable waterparty to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlandssigned, but not ratified: Marine Life ConservationLake Volta is the world's largest artificial lake (manmade reservoir) by surface area (8,482 sq km; 3,275 sq mi); the lake was created following the completion of the Akosombo Dam in 1965, which holds back the White Volta and Black Volta Rivers
People and Society :: GHANA
-
26,908,262note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 49noun: Ghanaian(s)adjective: GhanaianAkan 47.5%, Mole-Dagbon 16.6%, Ewe 13.9%, Ga-Dangme 7.4%, Gurma 5.7%, Guan 3.7%, Grusi 2.5%, Mande 1.1%, other 1.4% (2010 est.)Asante 16%, Ewe 14%, Fante 11.6%, Boron (Brong) 4.9%, Dagomba 4.4%, Dangme 4.2%, Dagarte (Dagaba) 3.9%, Kokomba 3.5%, Akyem 3.2%, Ga 3.1%, other 31.2%note: English is the official language (2010 est.)Christian 71.2% (Pentecostal/Charismatic 28.3%, Protestant 18.4%, Catholic 13.1%, other 11.4%), Muslim 17.6%, traditional 5.2%, other 0.8%, none 5.2% (2010 est.)Ghana has a young age structure, with approximately 57% of the population under the age of 25. Its total fertility rate fell significantly during the 1980s and 1990s but has stalled at around four children per woman for the last few years. Fertility remains higher in the northern region than the Greater Accra region. On average, desired fertility has remained stable for several years; urban dwellers want fewer children than rural residents. Increased life expectancy, due to better health care, nutrition, and hygiene, and reduced fertility have increased Ghana’s share of elderly persons; Ghana’s proportion of persons aged 60+ is among the highest in sub-Saharan Africa. Poverty has declined in Ghana, but it remains pervasive in the northern region, which is susceptible to droughts and floods and has less access to transportation infrastructure, markets, fertile farming land, and industrial centers. The northern region also has lower school enrollment, higher illiteracy, and fewer opportunities for women.Ghana was a country of immigration in the early years after its 1957 independence, attracting labor migrants largely from Nigeria and other neighboring countries to mine minerals and harvest cocoa – immigrants composed about 12% of Ghana’s population in 1960. In the late 1960s, worsening economic and social conditions discouraged immigration, and hundreds of thousands of immigrants, mostly Nigerians, were expelled.During the 1970s, severe drought and an economic downturn transformed Ghana into a country of emigration; neighboring Cote d’Ivoire was the initial destination. Later, hundreds of thousands of Ghanaians migrated to Nigeria to work in its booming oil industry, but most were deported in 1983 and 1985 as oil prices plummeted. Many Ghanaians then turned to more distant destinations, including other parts of Africa, Europe, and North America, but the majority continued to migrate within West Africa. Since the 1990s, increased emigration of skilled Ghanaians, especially to the US and the UK, drained the country of its health care and education professionals. Internally, poverty and other developmental disparities continue to drive Ghanaians from the north to the south, particularly to its urban centers.0-14 years: 38.2% (male 5,164,505/female 5,113,185)15-24 years: 18.66% (male 2,498,185/female 2,522,353)25-54 years: 34.05% (male 4,445,321/female 4,716,311)55-64 years: 4.91% (male 642,984/female 678,784)65 years and over: 4.19% (male 520,589/female 606,045) (2016 est.)total dependency ratio: 73%youth dependency ratio: 67.2%elderly dependency ratio: 5.9%potential support ratio: 17% (2015 est.)total: 21 yearsmale: 20.5 yearsfemale: 21.5 years (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1842.18% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 4030.8 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 387.1 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 133-1.9 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 161urban population: 54% of total population (2015)rate of urbanization: 3.4% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)Kumasi 2.599 million; ACCRA (capital) 2.277 million (2015)at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.01 male(s)/female15-24 years: 0.99 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.94 male(s)/female55-64 years: 0.95 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.86 male(s)/femaletotal population: 0.97 male(s)/female (2016 est.)22.6note: median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2014 est.)319 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 32total: 36.3 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 40.2 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 32.2 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 56total population: 66.6 yearsmale: 64.1 yearsfemale: 69.1 years (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 1724.03 children born/woman (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 3719.5% (2013)3.6% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 1330.1 physicians/1,000 population (2010)0.9 beds/1,000 population (2011)improved:urban: 92.6% of populationrural: 84% of populationtotal: 88.7% of populationunimproved:urban: 7.4% of populationrural: 16% of populationtotal: 11.3% of population (2015 est.)improved:urban: 20.2% of populationrural: 8.6% of populationtotal: 14.9% of populationunimproved:urban: 79.8% of populationrural: 91.4% of populationtotal: 85.1% of population (2015 est.)1.61% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 34274,600 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 2312,600 (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 26degree of risk: very highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: malaria, dengue fever, and yellow feverwater contact disease: schistosomiasisrespiratory disease: meningococcal meningitisanimal contact disease: rabies (2016)10.9% (2014)country comparison to the world: 14011% (2014)country comparison to the world: 556.2% of GDP (2014)country comparison to the world: 13definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 76.6%male: 82%female: 71.4% (2015 est.)total: 11 yearsmale: 12 yearsfemale: 11 years (2014)total number: 1,806,750percentage: 34% (2006 est.)total: 11.2%male: 10.2%female: 12% (2010 est.)
Government :: GHANA
-
conventional long form: Republic of Ghanaconventional short form: Ghanaformer: Gold Coastetymology: named for the medieval West African kingdom of the same name, but whose location was actually further north than the modern countrypresidential republicname: Accrageographic coordinates: 5 33 N, 0 13 Wtime difference: UTC 0 (5 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)10 regions; Ashanti, Brong-Ahafo, Central, Eastern, Greater Accra, Northern, Upper East, Upper West, Volta, Western6 March 1957 (from the UK)Independence Day, 6 March (1957)several previous; latest drafted 31 March 1992, approved and promulgated 28 April 1992, entered into force 7 January 1993; amended 1996 (2016)mixed system of English common law and customary lawhas not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdictioncitizenship by birth: nocitizenship by descent only: at least one parent or grandparent must be a citizen of Ghanadual citizenship recognized: yesresidency requirement for naturalization: 5 years18 years of age; universalchief of state: President Nana Addo Dankwa AKUFO-ADDO (since 7 January 2017); Vice President Mahamudu BAWUMIA (NPP) (since 7 January 2017); the president is both chief of state and head of governmenthead of government: President Nana Addo Dankwa AKUFO-ADDO (since 7 January 2017); Vice President Mahamudu BAWUMIA (NPP) (since 7 January 2017)cabinet: Council of Ministers; nominated by the president, approved by Parliamentelections/appointments: president and vice president directly elected on the same ballot by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 4-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 7 December 2016 (next to be held in December 2020)election results: Nana Addo Dankwa AKUFO-ADDO elected president; percent of vote - Nana Addo Dankwa AKUFO-ADDO (NPP) 54.1%, John Dramani MAHAMA (NDC) 44.0%, other 1.8%; note - results after 267 of 275 constituencies declareddescription: unicameral Parliament (275 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by simple majority vote to serve 4-year terms)elections: last held on 7 December 2016 (next to be held in December 2020)election results: percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - NDC 148, NPP 123, PNC 1, independent 3highest court(s): Supreme Court (consists of a chief justice and 12 justices)judge selection and term of office: chief justice appointed by the president in consultation with the Council of State (a small advisory body of prominent citizens) and with the approval of Parliament; other justices appointed by the president upon the advice of the Judicial Council (an 18-member independent body of judicial, military and police officials, and presidential nominees) and on the advice of the Council of State; justices can retire at age 60, with compulsory retirement at age 70subordinate courts: Court of Appeal; High Court; Circuit Court; District Court; regional tribunalsConvention People's Party or CPP [Samia NKRUMAH]National Democratic Congress or NDC [John Dramani MAHAMA]New Patriotic Party or NPP [Nana AFUKO-ADDO]People's National Convention or PNC [Hassan AYARIGA]note: listed are four of the more popular political parties as of December 2012; there are more than 20 registered partiesChristian Aid (water rights)Committee for Joint Action or CJA (social and economic issues)National Coalition Against the Privatization of Water or CAP (water rights)Oxfam (water rights)Public Citizen (water rights)Students Coalition Against EPA [Kwabena Ososukene OKAI] (education reform)Third World Network (social and economic issues)ACP, AfDB, AU, C, ECOWAS, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-24, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICC (national committees), ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, IMSO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO, ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, MINURSO, MINUSMA, MONUSCO, NAM, OAS (observer), OIF, OPCW, UN, UNAMID, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNIFIL, UNISFA, UNMIL, UNMISS, UNOCI, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTOchief of mission: Ambassador Lt. Gen. Joseph Henry SMITH (since September 2014)chancery: 3512 International Drive NW, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 686-4520FAX: [1] (202) 686-4527consulate(s) general: New Yorkchief of mission: Ambassador Robert P. JACKSON (since 4 February 2016)embassy: 24 Fourth Circular Rd., Cantonments, Accramailing address: P.O. Box 194, Accratelephone: [233] 030-274-1000FAX: [233] 030-274-1389three equal horizontal bands of red (top), yellow, and green, with a large black five-pointed star centered in the yellow band; red symbolizes the blood shed for independence, yellow represents the country's mineral wealth, while green stands for its forests and natural wealth; the black star is said to be the lodestar of African freedomnote: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia; similar to the flag of Bolivia, which has a coat of arms centered in the yellow bandblack star, golden eagle; national colors: red, yellow, green, blackname: "God Bless Our Homeland Ghana"lyrics/music: unknown/Philip GBEHOnote: music adopted 1957, lyrics adopted 1966; the lyrics were changed twice, in 1960 when a republic was declared and after a 1966 coup
Economy :: GHANA
-
Ghana's economy was strengthened by a quarter century of relatively sound management, a competitive business environment, and sustained reductions in poverty levels, but in recent years has suffered the consequences of loose fiscal policy, high budget and current account deficits, and a depreciating currency. Ghana has a market-based economy with relatively few policy barriers to trade and investment in comparison with other countries in the region, and Ghana is well-endowed with natural resources.Agriculture accounts for nearly one-quarter of GDP and employs more than half of the workforce, mainly small landholders. The services sector accounts for about half of GDP. Gold and cocoa exports, and individual remittances, are major sources of foreign exchange. Expansion of Ghana’s nascent oil industry has boosted economic growth, but the recent oil price crash reduced by half Ghana’s 2015 oil revenue. Production at Jubilee, Ghana's offshore oilfield, began in mid-December 2010 and currently produces roughly 110,000 barrels per day. The country’s first gas processing plant at Atubao is also producing natural gas from the Jubilee field, providing power to several of Ghana’s thermal power plants.As of 2015, the biggest single economic issue facing Ghana is the lack of consistent electricity. While the MAHAMA administration is taking steps to improve the situation, little progress has been made. Ghana signed a $920 million extended credit facility with the IMF in April 2015 to help it address its growing economic crisis. The IMF fiscal targets will require Ghana to reduce the fiscal deficit by cutting subsidies, decreasing the bloated public sector wage bill, strengthening revenue administration, and increasing revenues. The challenge for Ghana will come as the MAHAMA Administration approaches the November 2016 elections, facing public dissatisfaction in the midst of economic austerity.$120.8 billion (2016 est.)$116.9 billion (2015 est.)$112.5 billion (2014 est.)note: data are in 2016 dollarscountry comparison to the world: 82$42.76 billion (2015 est.)3.3% (2016 est.)3.9% (2015 est.)4% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 84$4,400 (2016 est.)$4,300 (2015 est.)$4,300 (2014 est.)note: data are in 2016 dollarscountry comparison to the world: 17416.1% of GDP (2016 est.)17.1% of GDP (2015 est.)17% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 113household consumption: 66.6%government consumption: 19.6%investment in fixed capital: 24.5%investment in inventories: 0.8%exports of goods and services: 36.7%imports of goods and services: -48.2% (2016 est.)agriculture: 19.5%industry: 24%services: 56.4% (2016 est.)cocoa, rice, cassava (manioc, tapioca), peanuts, corn, shea nuts, bananas; timbermining, lumbering, light manufacturing, aluminum smelting, food processing, cement, small commercial ship building, petroleum-0.5% (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 17611.99 million (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 48agriculture: 44.7%industry: 14.4%services: 40.9% (2013 est.)5.2% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 5724.2% (2013 est.)lowest 10%: 2%highest 10%: 32.8% (2006)42.3 (2012-13)41.9 (2005-06)country comparison to the world: 53revenues: $9.068 billionexpenditures: $11.55 billion (2016 est.)21.2% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 141-5.8% of GDP (2016 est.)country comparison to the world: 17473.7% of GDP (2016 est.)71.8% of GDP (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 40calendar year17.8% (2016 est.)17.2% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 21821% (31 December 2014)16% (31 December 2013)country comparison to the world: 431.8% (31 December 2016 est.)28.6% (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 6$5.914 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$5.736 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 95$13.02 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$12.42 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 102$13.39 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$12.93 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 98$3.465 billion (31 December 2012 est.)$3.097 billion (31 December 2011 est.)$3.531 billion (31 December 2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 92-$2.693 billion (2016 est.)-$2.836 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 156$10.25 billion (2016 est.)$10.36 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 87oil, gold, cocoa, timber, tuna, bauxite, aluminum, manganese ore, diamonds, horticultural productsIndia 25.2%, Switzerland 12.2%, China 10.6%, France 5.7% (2015)$13.73 billion (2016 est.)$13.47 billion (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 87capital equipment, refined petroleum, foodstuffsChina 32.6%, Nigeria 14%, Netherlands 5.5%, US 5.4% (2015)$6.137 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$5.885 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 88$21.17 billion (31 December 2016 est.)$19.15 billion (31 December 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 88$19.85 billion (31 December 2013 est.)$118 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 77$16.62 billion (31 December 2013 est.)$109 million (31 December 2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 55cedis (GHC) per US dollar -3.992 (2016 est.)3.712 (2015 est.)3.712 (2014 est.)2.895 (2013 est.)1.8 (2012 est.)
Energy :: GHANA
-
13 billion kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 929.2 billion kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 99500 million kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 7151 million kWh (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1052.847 million kW (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 9945.4% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1560% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 15054.6% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 440% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 210102,400 bbl/day (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 4398,700 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 3426,040 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 63660 million bbl (1 January 2016 es)country comparison to the world: 4510,640 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 10383,000 bbl/day (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 861,977 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 10872,850 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 6750 million cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 83650 million cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 930 cu m (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 163600 million cu m (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 6322.65 billion cu m (1 January 2016 es)country comparison to the world: 7411 million Mt (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 101
Communications :: GHANA
-
total subscriptions: 275,570subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 1 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 120total: 35.008 millionsubscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 133 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 42general assessment: primarily microwave radio relay; wireless local loop has been installed; outdated and unreliable fixed-line infrastructure heavily concentrated in Accradomestic: competition among multiple mobile-cellular providers has spurred growth with a subscribership of more than 130 per 100 persons and risinginternational: country code - 233; landing point for the SAT-3/WASC, Main One, and GLO-1 fiber-optic submarine cables that provide connectivity to South Africa, Europe, and Asia; satellite earth stations - 4 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean); microwave radio relay link to Panaf (2015)state-owned TV station, 2 state-owned radio networks; several privately owned TV stations and a large number of privately owned radio stations; transmissions of multiple international broadcasters are accessible; several cable and satellite TV subscriptio (2007).ghtotal: 6.181 millionpercent of population: 23.5% (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 68
Transportation :: GHANA
-
number of registered air carriers: 4inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 8annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 390,457annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 844,630 mt-km (2015)9G (2016)10 (2013)country comparison to the world: 156total: 7over 3,047 m: 12,438 to 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 3914 to 1,523 m: 2 (2013)total: 3914 to 1,523 m: 3 (2013)gas 394 km; oil 20 km; refined products 361 km (2013)total: 947 kmnarrow gauge: 947 km 1.067-m gauge (2014)country comparison to the world: 92total: 109,515 kmpaved: 13,787 kmunpaved: 95,728 km (2009)country comparison to the world: 451,293 km (168 km for launches and lighters on Volta, Ankobra, and Tano Rivers; 1,125 km of arterial and feeder waterways on Lake Volta) (2011)country comparison to the world: 56total: 4by type: petroleum tanker 1, refrigerated cargo 3foreign-owned: 2 (Brazil 1, South Korea 1) (2010)country comparison to the world: 133major seaport(s): Takoradi, Tema
Military and Security :: GHANA
-
Ghana Army, Ghana Navy, Ghana Air Force (2012)18-26 years of age for voluntary military service, with basic education certificate; no conscription; must be HIV/AIDS negative (2012)0.56% of GDP (2014)0.61% of GDP (2013)0.27% of GDP (2012)country comparison to the world: 125
Transnational Issues :: GHANA
-
disputed maritime border between Ghana and Cote d'Ivoirerefugees (country of origin): 11,419 (Cote d'Ivoire; flight from 2010 post-election fighting) (2016)current situation: Ghana is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; the trafficking of Ghanians, particularly children, internally is more common than the trafficking of foreign nationals; Ghanian children are subjected to forced labor in fishing, domestic service, street hawking, begging, portering, mining, quarrying, herding, and agriculture, with girls, and to a lesser extent boys, forced into prostitution; Ghanian women, sometimes lured with legitimate job offers, and girls are sex trafficked in West Africa, the Middle East, and Europe; Ghanian men fraudulently recruited for work in the Middle East are subjected to forced labor or prostitution, and a few Ghanian adults have been identified as victims of false labor in the US; women and girls from Vietnam, China, and neighboring West African countries are sex trafficked in Ghana; the country is also a transit point for sex trafficking from West Africa to Europetier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - Ghana does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; Ghana continued to investigate and prosecute trafficking offenses but was unable to ramp up its anti-trafficking efforts in 2014 because the government failed to provide law enforcement or protection agencies with operating budgets; victim protection efforts decreased in 2014, with significantly fewer victims identified; most child victims were referred to NGO-run facilities, but care for adults was lacking because the government did not provide any support to the country’s Human Trafficking Fund for victim services or its two shelters; anti-trafficking prevention measures increased modestly, including reconvening of the Human Trafficking Management Board, public awareness campaigns on child labor and trafficking, and anti-trafficking TV and radio programs (2015)illicit producer of cannabis for the international drug trade; major transit hub for Southwest and Southeast Asian heroin and, to a lesser extent, South American cocaine destined for Europe and the US; widespread crime and money-laundering problem, but the lack of a well-developed financial infrastructure limits the country's utility as a money-laundering center; significant domestic cocaine and cannabis use
