From left to right:
- The Altman Lab develops computational and informatics methods for understanding drug response — both toxicity and efficacy. They use machine learning, data mining and big and small data to look at drug response at all scales, from molecules to cells to tissues to patients to populations.
- The Delp Lab.
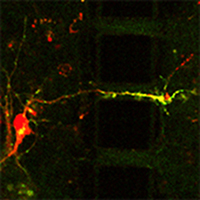
- The Lin Lab engineers optical and chemical tools to investigate nervous system function. Of primary interest are optical sensors of brain electrical activity, optical controllers of biochemical activities and chemical sensors of neuronal protein synthesis (pictured).
- Research in the Cardiovascular Biomechanics Computation Lab focuses on patient-specific computational modeling and simulation for cardiovascular disease. We develop and apply advanced algorithms for computational bioengineering, biofluid mechanics, optimization, fluid structure interaction and uncertainty quantification to high-impact clinical problems and disease progression. We have particular interests in pediatric and congenital heart disease, virtual surgery, biomedical device design and coronary artery disease.
The study of bioengineering applies the principles of engineering to the complexities of biological systems in a fusion of studies that promotes scientific discovery and the development of new biomedical technologies and therapies through research and education.
Research at Stanford Bioengineering seeks to record the world around us with utmost care and precision, to understand and recreate the phenomenon we witness and to design and develop tools with real and relevant applications. At its simplest, Stanford Bioengineering pivots on three pillars: Measure, Model, Make. With engineering as a paintbrush and biology as a canvas, Stanford Bioengineering seeks to not only understand, but to create.
Bioengineering research at Stanford can be visualized with this information matrix:
| MEASURE | MODEL | MAKE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| OF Biology | $1 origami microscope allows many thousands of people to discovery, learn about and study biology (Prakash Lab) | Mathematical model allows bioengineers to simulate behavior of an entire cell (Covert Lab) | Synthetic molecular motors engineered with gearshifts so that they can move in forward AND reverse (Bryant Lab) |
| FOR Biology | DNA sequencers detect what's happening inside people, from health of fetus to organ transplants to infections (Quake Lab) | Advanced algorithms allow better modeling and diagnostic detection in tissues using X-rays and MRI (Pelc Lab) | Light-responsive proteins engineered to control neurons, allowing study of brain, neurodisease and muscular systems (Deisseroth and Delp Labs) |
| WITH Biology | Engineered RNA sensors allow non-invasive detection of otherwise invisible metabolites (Smolke Lab) | Engineering cells and biomaterials to understand disease and enable tissue regeneration (Heilshorn Lab & Yang Lab) | Teenagers grow cell phone cases using mushrooms (BIOE.80; Endy & Liphardt) |




