Whole Blood
What is whole blood donation? A whole blood (WB) donation is the most common form of blood donation, in which a person gives one pint of blood.
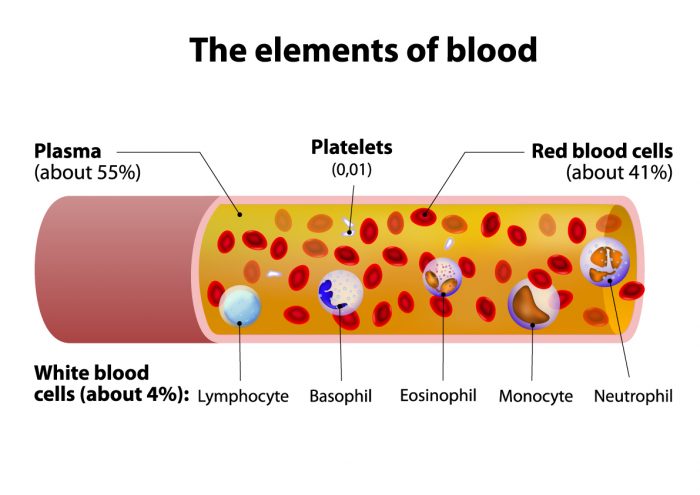
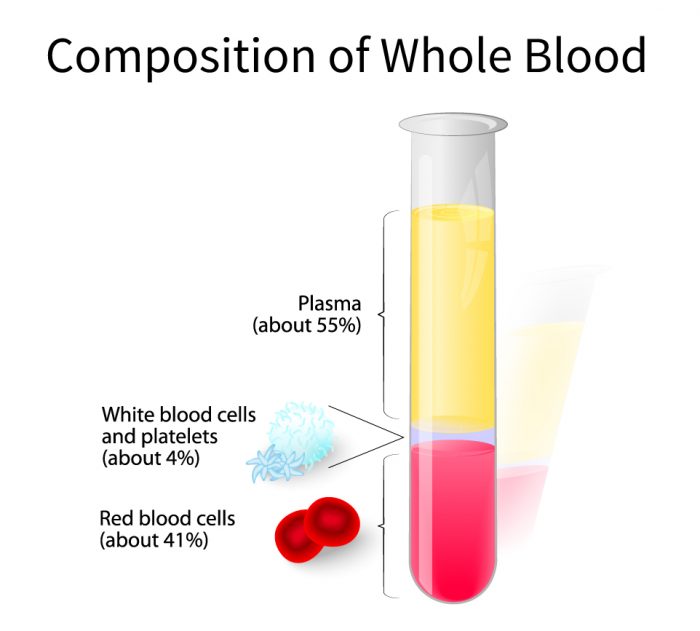
What is whole blood used for? After your donation, our lab separates the whole blood into its components. We do this because it allows us to deliver what patients need more specifically. The components we separate out are:
- Plasma: Many proteins in plasma that help with blood clotting come from the liver. It can be used for patients who have certain bleeding problems or in an emergent trauma situation.
- Red Blood Cells: Red blood cells transport oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and remove carbon dioxide and waste. Red blood cells are indicated for more than 70% of all transfusions. Patients who lose or at risk of losing significant volumes of blood require red blood cell transfusions. This population includes patients who have suffered severe trauma, have a perforated bleeding ulcer, or who are undergoing a major surgical procedure.
How long does donating take? The actual “draw” takes around 7 minutes, and the process overall takes about an hour. There are four basic steps in the whole blood donation process: registration, medical history, donation, and rest & refreshments. To learn more about what to expect when donating, click here.
What are the requirements for donating WB? To learn more about the requirements for donating whole blood, visit our eligibility page.
How often can I donate? You can donate whole blood every 56 days.
How do I make an appointment to donate? To make an appointment to donate whole blood, you can schedule online at sbcdonor.org or give us a call at 650-723-7831.
 Apheresis (Platelets, Plasma, and Double Red Blood Cells)
Apheresis (Platelets, Plasma, and Double Red Blood Cells)
What is apheresis blood collection? Apheresis blood collection, or ABC, is a special kind of blood donation. Instead of giving one pint of whole blood (as in a regular donation), an ABC donor gives only the components of blood needed for patients that day. ABC is made possible by an amazing machine that separates the components of your blood, retains certain components, and returns the rest to you—all with a single needle. It’s a very efficient way of directly helping patients in hospitals. By collecting the optimal number of blood components at each donation, we can help ensure that these lifesaving products are available for the community.
What are the requirements for apheresis blood collection? Each donation is based on gender, height, weight and hemoglobin (a value directly related to the number of red blood cells) count on the day of donation. These requirements are in place to ensure donor safety. One of our staff will use the blood collection machine and their expertise to determine what type of donation you can safely give that day. You may be recruited for an ABC donation on your first visit with us!
Why are the requirements different for women and men? Because women and men have different total blood volumes (TBV)—even if they weigh the same amount. The standard of care dictates that no more than 15% of a person’s TBV should be drawn at a time. Our apheresis machines determine TBV based on gender, height, weight and hemoglobin.
Platelets
What are platelets used for? Platelets, which come from the bone marrow, help to induce clotting and control bleeding. Patients who have been treated for leukemia with chemotherapy, for example, will often need to be transfused platelets.
What is the process of donating platelets? During a platelet donation, we will collect one, two, or three units of platelets. One of our medical technicians will recommend the number of units based on your weight, hemoglobin level, and platelet count that day.
How long does donating platelets take? Times for donating platelets can vary, but may take up to two hours.
How often can I donate platelets? You can donate platelets every 7 days. However, there is a limit to only 24 platelet donations each year.
Is there any special preparation required to donate platelets? Yes, there is. Please remember to increase intake of fluids, calcium, and iron at least two days before your appointment — this will help prevent donation reactions. Donors must be aspirin-free for 48 hours to donate platelets. This is because aspirin reduces the potency and performance of your platelets. The more time between taking aspirin and donating platelets, the better for the recipient.
Where can I donate platelets? Platelet donations are accepted at all three of our donor centers.
How do I know if I am eligible to donate platelets? To find out if you are eligible to donate platelets, make an appointment to donate whole blood, and ask your historian about platelets while you are there.
How do I make an appointment to donate? To make an appointment to donate platelets, give us a call at 650-723-7831.
 Plasma
Plasma
What is plasma used for? Much like platelets, plasma helps to induce clotting and control bleeding. However, it does this through different mechanisms and many of the clotting factors found in plasma are made from the liver. Therefore, although both plasma and platelets both help to control bleeding, they are sometimes used for different patient populations, depending on what the patient’s underlying disease.
How long does donating plasma take? Donations take 45-50 minutes.
How often can I donate plasma? You can donate plasma every four weeks. However, there is a limit to only 12 plasma donations each year.
Is there any special preparation required to donate plasma? To donate plasma, please remember to increase fluid and calcium intake, as well as iron.
Where can I donate plasma? Plasma donations are accepted at all three of our donor centers.
How do I make an appointment to donate? To make an appointment to donate plasma, give us a call at 650-723-7831.
Double Red Blood Cell Donation (DRBC)
What is double red blood cell donation? During a red blood cell donation, a machine is used to withdraw whole blood. Red cells are separated and retained, and the remainder of the blood is returned back to the donor. This donation safely removes twice as many red cells than traditional whole blood. We refer to this as a red cell donation, DRBC or T5 for short.
What are red blood cells used for? Red blood cells transport oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and remove carbon dioxide and waste. Red blood cells are indicated for more than 70% of all transfusions. Patients who lose or at risk of losing significant volumes of blood require red blood cell transfusions. This population includes patients who have suffered severe trauma, have a perforated bleeding ulcer, or who are undergoing a major surgical procedure.
What are the requirements for donating DRBC? Height, weight, and hemoglobin are crucial in determining whether a person can give this type of donation. In general, women must be at least 5′ 5″ tall and weigh at least 150 pounds, and men must be at least 5′ 1″ tall and weigh at least 130 pounds. DRBC donors must also have a hemoglobin level of at least 13.3 g/dL.
Why are the requirements different for women and men? Because women and men have different total blood volumes (TBV)—even if they weigh the same amount. The standard of care dictates that no more than 15% of a person’s TBV should be drawn at a time. Our apheresis machines determine TBV based on gender, height, weight and hemoglobin.
How long does donating take? The actual DRBC draw takes about 30 minutes.
Where can I donate?DRBC donations are accepted at all indoor mobile blood drives and all three fixed site locations: Palo Alto, Mountain View and Menlo Park.
How often can I donate? Donors may only give a DRBC donation every 16 weeks.
How do I make an appointment to donate? To make an appointment for a DRBC donation, give us a call at 650-723-7831.
