Introduction :: CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE
-
Upon independence in 1960, the former French region of Middle Congo became the Republic of the Congo. A quarter century of experimentation with Marxism was abandoned in 1990 and a democratically elected government took office in 1992. A brief civil war in 1997 restored former Marxist President Denis SASSOU-Nguesso, and ushered in a period of ethnic and political unrest. Southern-based rebel groups agreed to a final peace accord in March 2003. The Republic of Congo is one of Africa's largest petroleum producers, but with declining production it will need new offshore oil finds to sustain its oil earnings over the long term.
Geography :: CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE
-
Central Africa, bordering the South Atlantic Ocean, between Angola and Gabon
1 00 S, 15 00 E
Africa
total: 342,000 sq km
land: 341,500 sq km
water: 500 sq km
country comparison to the world: 64
slightly smaller than Montana
total: 5,008 km
border countries (5): Angola 231 km, Cameroon 494 km, Central African Republic 487 km, Democratic Republic of the Congo 1,229 km, Gabon 2,567 km
169 km
territorial sea: 12 nm
contiguous zone: 24 nm
exclusive economic zone: 200 nm
tropical; rainy season (March to June); dry season (June to October); persistent high temperatures and humidity; particularly enervating climate astride the Equator
coastal plain, southern basin, central plateau, northern basin
mean elevation: 430 m
elevation extremes: lowest point: Atlantic Ocean 0 m
highest point: Mount Berongou 903 m
petroleum, timber, potash, lead, zinc, uranium, copper, phosphates, gold, magnesium, natural gas, hydropower
agricultural land: 31.1%
arable land 1.6%; permanent crops 0.2%; permanent pasture 29.3%
forest: 65.6%
other: 3.3% (2011 est.)
20 sq km (2012)
seasonal flooding
air pollution from vehicle emissions; water pollution from raw sewage; tap water is not potable; deforestation
party to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertification, Endangered Species, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution, Tropical Timber 83, Tropical Timber 94, Wetlands
signed, but not ratified: none of the selected agreements
about 70% of the population lives in Brazzaville, Pointe-Noire, or along the railroad between them
People and Society :: CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE
-
4,852,412
note: estimates for this country explicitly take into account the effects of excess mortality due to AIDS; this can result in lower life expectancy, higher infant mortality, higher death rates, lower population growth rates, and changes in the distribution of population by age and sex than would otherwise be expected (July 2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 125
noun: Congolese (singular and plural)
adjective: Congolese or Congo
Kongo 48%, Sangha 20%, M'Bochi 12%, Teke 17%, Europeans and other 3%
French (official), Lingala and Monokutuba (lingua franca trade languages), many local languages and dialects (of which Kikongo is the most widespread)
Roman Catholic 33.1%, Awakening Churches/Christian Revival 22.3%, Protestant 19.9%, Salutiste 2.2%, Muslim 1.6%, Kimbanguiste 1.5%, other 8.1%, none 11.3% (2010 est.)
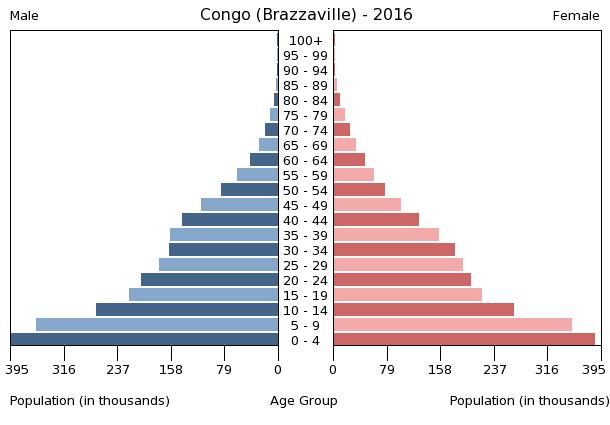
0-14 years: 41.53% (male 1,016,677/female 998,331)
15-24 years: 17.26% (male 419,248/female 418,397)
25-54 years: 34% (male 831,091/female 818,853)
55-64 years: 4.18% (male 101,118/female 101,879)
65 years and over: 3.03% (male 64,519/female 82,299) (2016 est.)
population pyramid:

Africa
::CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE

Population Pyramid
A population pyramid illustrates the age and sex structure of a country's population and may provide insights about political and social stability, as well as economic development. The population is distributed along the horizontal axis, with males shown on the left and females on the right. The male and female populations are broken down into 5-year age groups represented as horizontal bars along the vertical axis, with the youngest age groups at the bottom and the oldest at the top. The shape of the population pyramid gradually evolves over time based on fertility, mortality, and international migration trends.
For additional information, please see the entry for Population pyramid on the Definitions and Notes page under the References tab.
total dependency ratio: 86.2%
youth dependency ratio: 79.4%
elderly dependency ratio: 6.8%
potential support ratio: 14.7% (2015 est.)
total: 19.7 years
male: 19.6 years
female: 19.9 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 192
2.06% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 44
35.1 births/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
9.7 deaths/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 49
-4.8 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 191
urban population: 65.4% of total population (2015)
rate of urbanization: 3.22% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)
BRAZZAVILLE (capital) 1.888 million; Pointe-Noire 969,000 (2015)
at birth: 1.03 male(s)/female
0-14 years: 1.02 male(s)/female
15-24 years: 1 male(s)/female
25-54 years: 1.01 male(s)/female
55-64 years: 0.99 male(s)/female
65 years and over: 0.78 male(s)/female
total population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2016 est.)
19.8
note: median age at first birth among women 25-29 (2011/12 est.)
442 deaths/100,000 live births (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 16
total: 56.4 deaths/1,000 live births
male: 61.4 deaths/1,000 live births
female: 51.3 deaths/1,000 live births (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 24
total population: 59.3 years
male: 58.1 years
female: 60.6 years (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 201
4.63 children born/woman (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 21
44.7% (2011/12)
5.2% of GDP (2014)
country comparison to the world: 179
0.1 physicians/1,000 population (2007)
improved:
urban: 95.8% of population
rural: 40% of population
total: 76.5% of population
unimproved:
urban: 4.2% of population
rural: 60% of population
total: 23.5% of population (2015 est.)
improved:
urban: 20% of population
rural: 5.6% of population
total: 15% of population
unimproved:
urban: 80% of population
rural: 94.4% of population
total: 85% of population (2015 est.)
2.75% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 22
80,700 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 46
4,400 (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 34
degree of risk: very high
food or waterborne diseases: bacterial and protozoal diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fever
vectorborne disease: malaria and dengue fever
animal contact disease: rabies
water contact disease: schistosomiasis (2016)
9.7% (2014)
country comparison to the world: 163
12.3% (2015)
country comparison to the world: 61
6.2% of GDP (2010)
country comparison to the world: 39
definition: age 15 and over can read and write
total population: 79.3%
male: 86.4%
female: 72.9% (2015 est.)
total: 11 years
male: 11 years
female: 11 years (2012)
total number: 252,171
percentage: 25% (2005 est.)
Government :: CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE
-
conventional long form: Republic of the Congo
conventional short form: Congo (Brazzaville)
local long form: Republique du Congo
local short form: Congo
former: French Congo, Middle Congo, People's Republic of the Congo, Congo/Brazzaville
etymology: named for the Congo River, which makes up much of the country's eastern border; the river name derives from Kongo, a Bantu kingdom that occupied its mouth at the time of Portuguese discovery in the late 15th century and whose name stems from its people the Bakongo, meaning "hunters"
presidential republic
name: Brazzaville
geographic coordinates: 4 15 S, 15 17 E
time difference: UTC+1 (6 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)
12 departments (departments, singular - department); Bouenza, Brazzaville, Cuvette, Cuvette-Ouest, Kouilou, Lekoumou, Likouala, Niari, Plateaux, Pointe-Noire, Pool, Sangha
15 August 1960 (from France)
Independence Day, 15 August (1960)
previous 1992; latest approved by referendum 20 January 2002; amended 2015; note - the constitutional referendum approved in October 2015 changed the head of government from the president to the prime minister, eliminated the presidential age maximum, reduced the presidential term from 7 to 5 years and limited total presidential terms to 3 (2017)
mixed legal system of French civil law and customary law
has not submitted an ICJ jurisdiction declaration; accepts ICCt jurisdiction
citizenship by birth: no
citizenship by descent only: at least one parent must be a citizen of the Republic of the Congo
dual citizenship recognized: no
residency requirement for naturalization: 10 years
18 years of age; universal
chief of state: President Denis SASSOU-Nguesso (since 25 October 1997)
head of government: Prime Minister Clement MOUAMBA (since 23 April 2016); note - a constitutional referendum held in 2015 approved the change of the head of government from the president to the prime minister
cabinet: Council of Ministers appointed by the president
elections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for 2 additional terms); election last held on 20 March 2016 (next to be held in 2021)
election results: Denis SASSOU-Nguesso reelected president; percent of vote - Denis SASSOU-Nguesso (PCT) 60.4%, Guy Price Parfait KOLELAS (MCDDI) 15.1%, Jean-Marie MOKOKO (independent) 13.9%, Pascal Tsaty MABIALA (UPADS) 4.4%, other 6.2%
description: bicameral Parliament or Parlement consists of the Senate (72 seats; members indirectly elected by regional councils by simple majority vote to serve 6-year terms with one-half of membership renewed every three years) and the National Assembly (139 seats; members directly elected in single-seat constituencies by absolute majority popular vote in two rounds if needed; members serve 5-year terms)
elections: Senate - last held on 12 October 2014 for 36 of the expiry seats (next to be held in 2020); National Assembly - last held on 15 July and 5 August 2012 (next to be held in July 2017)
election results: Senate - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - RMP 33, FDU 23, UPADS 2, other 7, independent 7; National Assembly - percent of vote by party - NA; seats by party - PCT 89, MCDDI 7, UPADS 7, RDPS 5, MAR 4, RC 3, MUST 2, UPDP 2, CPR 1, PRL 1, PUR 1, UFD 1, UR 1, independent 12, vacant 3
highest court(s): Supreme Court or Cour Supreme (consists of NA judges); Constitutional Court (consists of 9 members); note - a High Court of Justice, outside the judicial authority, tries cases involving treason by the president of the republic
judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court judges elected by Parliament and serve until age 65; Constitutional Court members appointed by the president of the republic - 3 directly by the president and 6 nominated by Parliament; members appointed for renewable 9-year terms with one-third of the membership renewed every 3 years
subordinate courts: Court of Audit and Budgetary Discipline; courts of appeal; regional and district courts; employment tribunals; juvenile courts;
Action Movement for Renewal or MAR [Roland BOUITI-VIAUDO]
Citizen's Rally or RC
Congolese Labour Party or PCT [Denis SASSOU-NGUESSO]
Congolese Movement for Democracy and Integral Development or MCDDI [Guy Price Parfait KOLELAS]
Movement for Unity, Solidarity, and Work or MUST [Claudine MUNARI]
Pan-African Union for Social Development or UPADS [Pascal Tsaty MABIALA]
Party for the Unity of the Republic or PUR
Patriotic Union for Democracy and Progress or UPDP [Auguste-Celestin GONGARD NKOUA
Prospects and Realities Club or CPR
Rally for Democracy and Social Progress or RDPS [Bernard BATCHI]
Rally of the Presidential Majority or RMP
Republican and Liberal Party or PRL
Union for the Republic or UR
Union of Democratic Forces
Union for Democracy and Republic or UDR
United Democratic Forces or FDU [Sebastian EBAO]; many smaller parties
Congolese Trade Union Congress or CSC
General Union of Congolese Pupils and Students or UGEEC
Revolutionary Union of Congolese Women or URFC
Union of Congolese Socialist Youth or UJSC
ACP, AfDB, AU, BDEAC, CEMAC, EITI (compliant country), FAO, FZ, G-77, IAEA, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ISO (correspondent), ITSO, ITU, ITUC (NGOs), MIGA, NAM, OIF, OPCW, UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNHCR, UNIDO, UNITAR, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WFTU (NGOs), WHO, WIPO, WMO, WTO
chief of mission: Ambassador Serge MOMBOULI (since 31 July 2001)
chancery: 1720 16th Street NW, Washington, DC 20009
telephone: [1] (202) 726-5500
FAX: [1] (202) 726-1860
chief of mission: Ambassador Stephanie S. SULLIVAN (since 12 August 2013)
embassy: 70-83 Section D, Maya-Maya Boulevard, Brazzaville
mailing address: B.P. 1015, Brazzaville
telephone: [242] 06 612-2000
divided diagonally from the lower hoist side by a yellow band; the upper triangle (hoist side) is green and the lower triangle is red; green symbolizes agriculture and forests, yellow the friendship and nobility of the people, red is unexplained but has been associated with the struggle for independence
note: uses the popular Pan-African colors of Ethiopia
lion, elephant; national colors: green, yellow, red
name: "La Congolaise" (The Congolese)
lyrics/music: Jacques TONDRA and Georges KIBANGHI/Jean ROYER and Joseph SPADILIERE
note: originally adopted 1959, restored 1991
Economy :: CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE
-
The economy is a mixture of subsistence farming and hunting, an industrial sector based largely on oil and support services, and government spending. Oil has supplanted forestry as the mainstay of the economy, providing a major share of government revenues and exports. Natural gas is increasingly being converted to electricity rather than being flared, greatly improving energy prospects. New mining projects, particularly iron ore, which entered production in late 2013, may add as much as $1 billion to annual government revenue.
Economic reform efforts have been undertaken with the support of international organizations, notably the World Bank and the IMF, including the recently concluded Article IV consultations. The current administration faces difficult economic challenges of stimulating recovery and reducing poverty. The recent drop in oil prices has constrained government spending; lower oil prices forced the government to cut more than $1 billion in planned spending. However, the government increased infrastructure spending for the September 2015 All-Africa Games and also ahead of the March 2016 presidential election, putting further pressure on the budget.
Officially the country became a net external creditor as of 2011, with external debt representing only about 16% of GDP and debt servicing less than 3% of government revenue.
$30.27 billion (2016 est.)
$29.75 billion (2015 est.)
$29.08 billion (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 131
$8.834 billion (2015 est.)
1.7% (2016 est.)
2.3% (2015 est.)
6.8% (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
$6,800 (2016 est.)
$6,800 (2015 est.)
$6,800 (2014 est.)
note: data are in 2016 dollars
country comparison to the world: 156
22.1% of GDP (2016 est.)
12.4% of GDP (2015 est.)
38.9% of GDP (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 66
household consumption: 50%
government consumption: 10.5%
investment in fixed capital: 48.7%
investment in inventories: 0.2%
exports of goods and services: 44.5%
imports of goods and services: -53.9% (2016 est.)
agriculture: 4.9%
industry: 69.8%
services: 25.3% (2016 est.)
cassava (manioc, tapioca), sugar, rice, corn, peanuts, vegetables, coffee, cocoa; forest products
petroleum extraction, cement, lumber, brewing, sugar, palm oil, soap, flour, cigarettes
3.5% (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 68
1.807 million (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 124
53% (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 203
46.5% (2011 est.)
lowest 10%: 2.1%
highest 10%: 37.1% (2005)
revenues: $3.562 billion
expenditures: $4.233 billion (2016 est.)
40.3% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 39
-7.6% of GDP (2016 est.)
country comparison to the world: 189
49.3% of GDP (2016 est.)
48% of GDP (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
calendar year
2.3% (2016 est.)
2.6% (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 121
4.25% (31 December 2009)
4.75% (31 December 2008)
country comparison to the world: 87
14% (31 December 2016 est.)
14.8% (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 50
$3.274 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$3.131 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
$4.875 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
$4.858 billion (31 December 2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
$1.825 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$1.807 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
$NA
-$728 million (2016 est.)
-$1.861 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 113
$4.777 billion (2016 est.)
$5.231 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 107
petroleum, lumber, plywood, sugar, cocoa, coffee, diamonds
China 42.1%, Italy 16.9%, US 4.9%, India 4.7%, Portugal 4.2% (2015)
$3.447 billion (2016 est.)
$3.934 billion (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 135
capital equipment, construction materials, foodstuffs
China 20.3%, France 14.2%, South Korea 9.8%, US 4.9%, UK 4.4%, Italy 4.1%, India 4.1% (2015)
$1.989 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$2.244 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 115
$4.817 billion (31 December 2016 est.)
$4.324 billion (31 December 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
Cooperation Financiere en Afrique Centrale francs (XAF) per US dollar -
589.4 (2016 est.)
591.45 (2015 est.)
591.45 (2014 est.)
494.42 (2013 est.)
510.53 (2012 est.)
Energy :: CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE
-
1.7 billion kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 142
900 million kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 157
22 million kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 91
18 million kWh (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 112
500,000 kW (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 148
12.2% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 197
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 183
87.8% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 15
0% of total installed capacity (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 131
269,000 bbl/day (2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 33
252,300 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 27
0 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 193
1.6 billion bbl (1 January 2016 es)
country comparison to the world: 38
18,550 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 94
16,000 bbl/day (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 147
5,426 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 93
2,615 bbl/day (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 182
1.5 billion cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 60
1.5 billion cu m (2014 est.)
country comparison to the world: 85
39 million cu m (2012 est.)
country comparison to the world: 51
0 cu m (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 134
90.61 billion cu m (1 January 2016 es)
country comparison to the world: 55
6.5 million Mt (2013 est.)
country comparison to the world: 123
Communications :: CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE
-
total subscriptions: 17,000
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 193
total: 5.216 million
subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 110 (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 118
general assessment: primary network consists of microwave radio relay and coaxial cable with services barely adequate for government use; key exchanges are in Brazzaville, Pointe-Noire, and Loubomo; intercity lines frequently out of order
domestic: fixed-line infrastructure inadequate, providing less than 1 connection per 100 persons; in the absence of an adequate fixed-line infrastructure, mobile-cellular subscribership has surged to 110 per 100 persons
international: country code - 242; satellite earth station - 1 Intelsat (Atlantic Ocean) (2015)
1 state-owned TV and 3 state-owned radio stations; several privately owned TV and radio stations; satellite TV service is available; rebroadcasts of several international broadcasters are available (2007)
.cg
total: 362,000
percent of population: 7.6% (July 2015 est.)
country comparison to the world: 171
Transportation :: CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE
-
number of registered air carriers: 3
inventory of registered aircraft operated by air carriers: 12
annual passenger traffic on registered air carriers: 657,926
annual freight traffic on registered air carriers: 2,987,493 mt-km (2015)
TN (2016)
27 (2013)
country comparison to the world: 125
total: 8
over 3,047 m: 2
2,438 to 3,047 m: 1
1,524 to 2,437 m: 5 (2013)
total: 19
1,524 to 2,437 m: 8
914 to 1,523 m: 9
under 914 m: 2 (2013)
gas 232 km; liquid petroleum gas 4 km; oil 982 km (2013)
total: 510 km
narrow gauge: 510 km 1.067-m gauge (2014)
country comparison to the world: 113
total: 17,000 km
paved: 1,212 km
unpaved: 15,788 km (2006)
country comparison to the world: 119
1,120 km (commercially navigable on Congo and Oubanqui Rivers above Brazzaville; there are many ferries across the river to Kinshasa; the Congo south of Brazzaville-Kinshasa to the coast is not navigable because of rapids, necessitating a rail connection to Pointe Noire; other rivers are used for local traffic only) (2011)
country comparison to the world: 61
registered in other countries: 1 (Democratic Republic of the Congo 1) (2010)
country comparison to the world: 148
major seaport(s): Pointe-Noire
river port(s): Brazzaville (Congo); Impfondo (Oubangi); Ouesso (Sangha); Oyo (Alima)
oil terminal(s): Djeno
Military and Security :: CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE
-
Congolese Armed Forces (Forces Armees Congolaises, FAC): Army (Armee de Terre), Navy, Congolese Air Force (Armee de l'Air Congolaise); Gendarmerie; Special Presidential Security Guard (GSSP) (2013)
18 years of age for voluntary military service; women may serve in the Armed Forces (2012)
Transnational Issues :: CONGO, REPUBLIC OF THE
-
the location of the boundary in the broad Congo River with the Democratic Republic of the Congo is undefined except in the Pool Malebo/Stanley Pool area
refugees (country of origin): 8,549 (Rwanda) (2015); 29,304 (Central African Republic); 12,223 (Democratic Republic of the Congo) (2016)
IDPs: 7,800 (multiple civil wars since 1992) (2015)
current situation: the Republic of the Congo is a source and destination country for children, men, and women, subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; most trafficking victims are from Benin, the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC), and, to a lesser extent, other neighboring countries and are subjected to domestic servitude and market vending by West African and Congolese nationals; adults and children, the majority from the DRC, are also sex trafficked in Congo, mainly Brazzaville; internal trafficking victims, often from rural areas, are exploited as domestic servants or forced to work in quarries, bakeries, fishing, and agriculture
tier rating: Tier 2 Watch List - the Republic of the Congo does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; the country drafted an action plan based on anti-trafficking legislation, which remains pending in the Supreme Court; the government made minimal anti-trafficking law enforcement efforts in 2014, failing to prosecute or convict suspected traffickers from cases dating back to 2010; serious allegations of official complicity continue to be reported; the government lacks a systematic means of identifying victims and relies on NGOs and international organizations to identify victims and NGOs and foster families to provide care to victims; the quality of care varied widely because the foster care system was allegedly undermined by inadequate security and official complicity (2015)