Education
What is blood?
Blood is a living tissue composed of blood cells suspended in plasma.
The cellular elements -- red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets -- make up about 45% of the volume of whole blood. Plasma, which is 92% water, makes up the remaining 55%.
Blood accounts for approximately 7% of a person’s weight. An average sized man has about 12 pints of blood, and an average sized woman has about 9 pints. When you donate blood, your body immediately begins replacing the donated blood volume, so you can safely donate as often as 6 times a year.
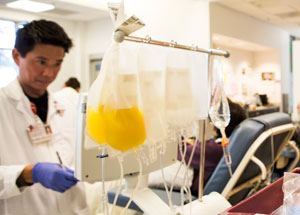
Manny Dy, Apheresis Technician, with platelets that can be used to treat cancer patients, bone marrow transplant patients, trauma victims, and patients with blood disorders.
Components of blood
- Red blood cells transport oxygen and nutrients to the tissues and remove carbon dioxide and waste. Red blood cells are indicated for more than 70% of all transfusions. Accident victims, patients with ulcers and patients undergoing surgery use red blood cells.
- Platelets act to induce clotting and control bleeding.
- Plasma is 92% water, miscellaneous elements and 7% protein from which derivatives are made. Cryoprecipitate, antihemophilic factor and fresh frozen plasma can be given to patients who have hemophilia and other bleeding problems. Gamma Globulin is used to supplement the immune system in fighting disease such as hepatitis, and serum albumin is given to treat and prevent shock.
- White blood cells protect the body against disease and infection. They move through the blood stream to attack and absorb bacteria and other "foreign" bodies. Since white blood cells are likely to cause a negative reaction in blood recipients, these cells are removed from the blood donation and used for research.

