Mannequin-based Patient Simulation
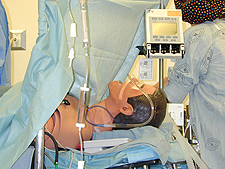
Taking the underlying concepts described for the desktop simulation one step further is the recreation of the real physical patient in a realistic physical clinical environment. This is done because real patients don’t live in a virtual world – they and the clinicians who care for them work in an actual physical world with real people. Thus, computerized mannequin stands in for the patient, and a variety of equipment can be used (either real clinical equipment or computer-driven replicas) to monitor and treat the patient.

The mannequin-based simulator has a computer representation of the patient similar to that in a desktop simulator, replacing the videos, drawings, and animations with actual functions of the “plastic person.” Among the functions that these mannequin-based simulators can replicate are:
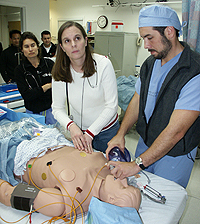
- Spontaneous breathing (and the ability to breathe for the patient with a bag or ventilator)
- Real-time display of electronically monitored information (e.g. ECG, oxygen saturation, etc.)
- Pulses, heart sounds, breath sounds, pupil size, pupil response to light
- Obstruction of various parts of the airway
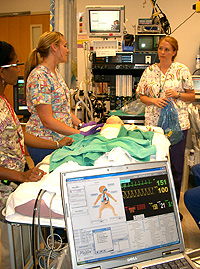
Not only are these created in their “normal” manifestation, but all the elements of a large variety of abnormal conditions can be created such as (the list is almost endless) heart attack, severe allergic reaction, breathing difficulties, sepsis (“blood poisoning”), severe abnormalities of sugar metabolism, etc.
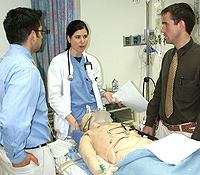
Some simulators contain complex models of the effects that many different drugs will have, tracking the distribution of the drug in the body and calculating the particular effect that a specific amount of drug will have on the different bodily functions. Most of these simulators provide the ability to stick tubes and needles into various places and to perform other invasive maneuvers such as “shocking the heart” (debrillation) or applying an external pacemaker.
Mannequin-based simulators typically include speakers in or near the patient’s head so that the mannequin is also a Standardized Patient actor. The voice of the patient can come from the computer, or from an instructor or actor using a microphone. Having an SP that can get seriously ill or die – without complaining – is a real advantage in some settings.
Mannequin-based simulators have become very common in many fields (operating room, intensive care unit, emergency department, labor and delivery rooms) where life-threatening situations require prompt recognition and treatment by individuals or teams of clinicians. Simulations can be conducted in a dedicated simulation learning facility, or portable simulated patients can be taken to empty clinical spots in a real work unit (say a real ICU) where simulation exercises can be conducted in the actual places that patient care is done. These simulators are used across all levels of learners, from K-12 students to early learners in university or medical or nursing school, and by experienced personnel both as individuals, groups, and full multidisciplinary teams. Not only are lessons learned by and about the people in the simulations, lessons are also learned about clinical work units and “systems”. These lessons can be turned into effective improvements in the workplace and beneficial changes in how we take care of patients in the future.

