New & Noteworthy
New SGD Help Video: Variant Viewer
November 5, 2015
Using SGD’s Variant Viewer, you can compare the nucleotide and protein sequences of your favorite genes in twelve widely-used S. cerevisiae genomes. This tool shows alignments, similarity scores, and sequence variants for open reading frames (ORFs) from the different strains relative to the S288C reference genome. Sequence data are derived from Song et al., 2015.
Take a look at our new video tutorial to get started with the Variant Viewer, and let us know if you have questions or suggestions.
Reference Genome Annotation Update R64.2.1
February 23, 2015
SGD curators periodically update the chromosomal annotations of the S. cerevisiae Reference Genome, which is derived from strain S288C. Last November, the genome annotation was updated for the first time since the release of the major S288C resequencing update in February 2011. Note that the underlying sequence of 16 assembled nuclear chromosomes, plus the mitochondrial genome, remained unchanged in annotation release R64.2.1 (relative to genome sequence release R64.1.1).
The R64.2.1 annotation release included various updates and additions. The annotations of 2 existing proteins changed (GRX3/YDR098C and HOP2/YGL033W), and 1 new ORF (RDT1/YCL054W-A) and 4 RNAs (RME2, RME3, IRT1, ZOD1) were added to the genome annotation. Other additions include 8 nuclear matrix attachment sites, and 8 mitochondrial origins of replication. The coordinates of many autonomously replicating sequences (ARS) were updated, and many new ARS consensus sequences were added. Complete details can be found in the Summary of Chromosome Sequence and Annotation Updates.
New Alternative Reference Genomes
December 8, 2014
At SGD, we are expanding our scope to provide annotation and comparative analyses of all major budding yeast strains, and are making progress in our move toward providing multiple reference genomes. To this end, the following new S. cerevisiae genomes have been incorporated into SGD as “Alternative References”: CEN.PK, D273-10B, FL100, JK9-3d, RM11-1a, SEY6210, SK1, Sigma1278b, W303, X2180-1A, Y55. These genomes are accessible via Sequence, Strain, and Contig pages, and are the genomes for which we have curated the most phenotype data, and for which we aim to curate specific functional information. It is important to emphasize that we are not abandoning a standard sequence; S288C is still in place as “The Reference Genome”. However, we do recognize that it is helpful for students and researchers to be able to ‘shift the reference’, selecting the genome that is most appropriate and informative for a specific area of study.
These new genome sequences have been also been added to SGD’s BLAST datasets, multiple sequence alignments, the Pattern Matching tool, and the Downloads site. Please explore these new genomes, and send us your feedback.
Tags: reference genome > Saccharomyces cerevisiae > strains
New Sequence, Chromosome, and Contig pages
August 25, 2014
New Sequence pages are now available in SGD for virtually every yeast gene (e.g., HMRA1 Sequence page), and include genomic sequence annotations for the Reference Strain S288C, as well as several Alternative Reference Genomes from strains such as CEN.PK, RM11-1a, Sigma1278b, and W303 (more Alternative References coming soon). Each page includes an Overview section containing descriptive information, maps depicting genomic context in Reference Strain S288C (as shown below) and Alternative Reference strains, as well as chromosomal and relative coordinates in S288C.

The sequence itself includes display options for genomic DNA, coding DNA, or translated protein.
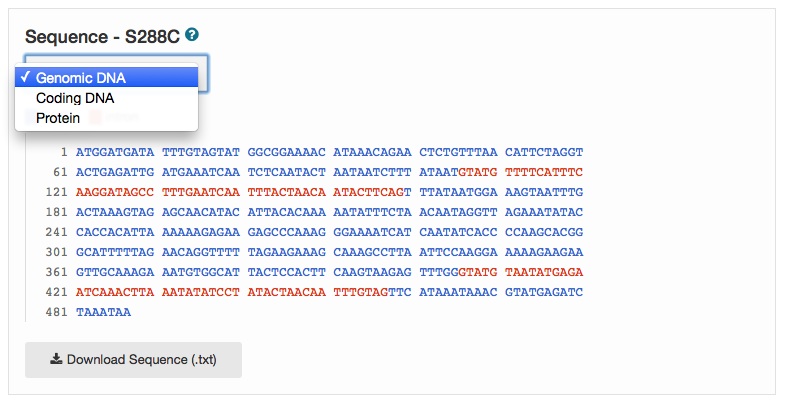
Also available on each Sequence page are links to redesigned S288C Chromosome pages, links to new Contig pages for Alternative Reference Genomes, and a Downloads menu for easy access to DNA sequences of several other industrial strains and environmental isolates. The new Sequence, Chromosome, and Contig pages make use of many of the features you enjoy on other new or redesigned pages at SGD, including graphical display of data, sortable tables, and responsive visualizations. The Sequence pages also provide seamless access to other tools at SGD such as BLAST and Web Primer. Please explore these new pages, accessible via the Sequence tab on your favorite Locus Summary page, and send us your feedback.